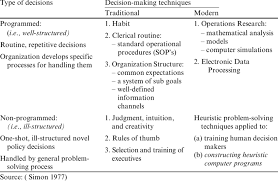
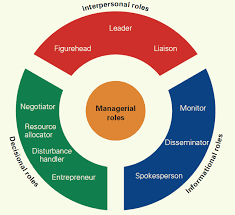
Title: The Art of Decision Making in Business Management
Introduction:
In the fast-paced and competitive world of business management, effective decision making is a crucial skill that can make or break an organization. Every day, leaders and managers are faced with countless choices that have the potential to shape the future of their companies. This article explores the importance of decision making in business management and provides insights into effective strategies for making informed and successful decisions.
The Impact of Decision Making:
Decisions made by business managers have far-reaching consequences, influencing various aspects such as profitability, productivity, employee morale, customer satisfaction, and overall organizational success. A well-made decision can propel a company forward, while a poor one can lead to setbacks and missed opportunities.
Gathering Information:
To make informed decisions, it is essential to gather relevant information from reliable sources. This includes analyzing market trends, conducting market research, studying competitors’ strategies, and considering internal factors such as financial data and performance metrics. By having access to accurate information, managers can assess risks and opportunities more effectively.
Weighing Options:
In business management, decision makers often face multiple options or alternatives. It is crucial to evaluate each option carefully by considering factors such as feasibility, cost-effectiveness, potential risks and rewards, alignment with organizational goals, and long-term implications. Employing tools like SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) can aid in comparing options objectively.
Involving Stakeholders:
Effective decision making involves considering the perspectives and input of key stakeholders within the organization. Engaging employees at different levels fosters a sense of ownership and encourages diverse viewpoints that may uncover valuable insights or identify potential pitfalls before finalizing decisions.
Risk Assessment:
Every decision carries an inherent level of risk. Business managers must assess risks associated with each option by evaluating their probability of occurrence and potential impact on the organization’s objectives. Strategies like risk mitigation, contingency planning, and scenario analysis can help minimize potential negative outcomes.
Time Management:
In the fast-paced business environment, time is a critical factor. While some decisions require immediate action, others benefit from careful deliberation. Effective decision makers strike a balance between promptness and thoroughness, ensuring that decisions are made in a timely manner without compromising their quality.
Learning from Mistakes:
Even the most experienced business managers make mistakes. It is essential to view failures as learning opportunities rather than setbacks. Analyzing unsuccessful decisions can provide valuable insights for future decision making, helping managers refine their strategies and avoid repeating past errors.
Conclusion:
Decision making in business management is an art that combines analytical thinking, strategic planning, and intuition. Successful leaders understand that decisions impact not only their organizations but also stakeholders at large. By employing informed decision-making processes, considering multiple perspectives, and learning from both successes and failures, business managers can navigate uncertainties and propel their organizations towards sustainable growth and success.
Frequently Asked Questions About Decision Making in Business Management
- What are the 5 process of decision-making?
- Why decision-making is important in business management?
- What are the 4 types of decision-making?
- What are the 3 types of decision-making in business?
What are the 5 process of decision-making?
The decision-making process typically involves several steps or stages. While different models may have slight variations, here are the five commonly recognized processes of decision-making:
Identifying and Defining the Problem:
The first step is to clearly identify and define the problem or the decision that needs to be made. This involves understanding the underlying issue, gathering relevant information, and determining the desired outcome.
Gathering Information and Analyzing Options:
Once the problem is identified, it’s crucial to gather as much information as possible about the available options. This may involve conducting research, seeking expert advice, evaluating data, and considering various perspectives. Analyzing these options helps in understanding their potential benefits, risks, costs, and implications.
Evaluating Alternatives:
In this stage, decision makers compare and evaluate different alternatives or courses of action based on criteria such as feasibility, effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, alignment with goals, and potential outcomes. Tools like SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) or decision matrices can assist in objectively assessing alternatives.
Making a Decision:
After carefully evaluating all available options, a decision needs to be made. This involves selecting one alternative that best aligns with the desired outcome and provides the greatest benefit for the organization or individual involved. The chosen option should consider both short-term and long-term implications.
Implementing and Reviewing:
Once a decision is made, it must be implemented effectively by developing an action plan and allocating necessary resources. Regular monitoring of progress is essential to ensure that the decision achieves its intended objectives. If needed, adjustments can be made along the way based on feedback and evaluation results.
It’s important to note that decision-making is often an iterative process where feedback from implementation informs future decisions or adjustments if necessary. Additionally, involving stakeholders throughout these steps can enhance collaboration and increase acceptance of decisions made within an organization or group setting.
Why decision-making is important in business management?
Decision-making is of paramount importance in business management for several reasons:
- Strategic Direction: Effective decision-making sets the strategic direction for an organization. It helps define goals, objectives, and the path to achieve them. By making well-informed decisions, managers can align their actions with the overall vision of the company and ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
- Resource Optimization: Business management involves allocating resources such as finances, personnel, and time effectively. Decision-making plays a crucial role in determining how these resources are utilized to maximize productivity and profitability. By making sound decisions, managers can optimize resource allocation and minimize waste.
- Risk Mitigation: Every business decision carries a certain degree of risk. Decision-making allows managers to assess potential risks associated with various options and develop strategies to mitigate them. By carefully weighing risks and rewards, managers can make informed choices that minimize potential negative outcomes.
- Adaptability: In today’s dynamic business environment, adaptability is key to survival and success. Effective decision-making enables managers to respond quickly and effectively to changes in market conditions, customer demands, or industry trends. It allows organizations to stay agile and seize opportunities as they arise.
- Employee Engagement: Involving employees in decision-making processes fosters a sense of ownership and engagement within the organization. When employees feel valued and included in decision-making, they become more motivated, productive, and committed to achieving organizational goals.
- Customer Satisfaction: Decision-making directly impacts customer satisfaction levels. By making customer-centric decisions based on market research and feedback, managers can enhance products or services, improve customer experiences, and build long-term loyalty.
- Competitive Advantage: Effective decision-making gives businesses a competitive edge by enabling them to identify unique opportunities or innovative solutions before their competitors do. It allows organizations to differentiate themselves from others in the market by making strategic choices that resonate with customers.
- Long-Term Success: Consistent effective decision-making is crucial for the long-term success and sustainability of a business. It helps managers build a track record of making sound choices, which enhances credibility and trust among stakeholders, including investors, employees, customers, and partners.
In conclusion, decision-making is essential in business management because it sets strategic direction, optimizes resource allocation, mitigates risks, fosters adaptability, engages employees, enhances customer satisfaction, provides a competitive advantage, and ensures long-term success. By making informed and effective decisions, managers can steer their organizations towards growth and profitability in an ever-changing business landscape.
What are the 4 types of decision-making?
There are several different models and classifications of decision-making, but one commonly used framework identifies four types of decision-making:
- Routine decisions: These are the everyday decisions that we make as part of our daily routines. They are typically low-risk and have minimal impact on our lives or organizations. Routine decisions often follow established procedures or guidelines, requiring little time or effort to make.
- Tactical decisions: Tactical decisions are medium-term decisions that involve choosing between different alternatives to achieve specific goals or objectives. These decisions require more analysis and evaluation than routine decisions but are still relatively straightforward. Examples include determining marketing strategies, resource allocation, or operational planning.
- Strategic decisions: Strategic decisions are long-term, high-impact decisions that shape the overall direction and vision of an organization. They involve significant resources and have far-reaching consequences for the company’s future success. Strategic decision-making requires careful analysis, consideration of various factors such as market trends, competitive landscape, and internal capabilities.
- Crisis decisions: Crisis decisions are made in response to unexpected events or emergencies that require immediate action. These situations often involve high levels of stress and uncertainty, requiring quick thinking and decisive action to mitigate risks and minimize negative impacts.
It’s important to note that these categories can overlap, as decision-making processes can vary depending on the specific context and complexity of the situation. Additionally, some decision-making models may include additional types or variations based on specific criteria or industry-specific requirements.
What are the 3 types of decision-making in business?
In business, decision-making can be categorized into three main types:
Strategic Decision Making:
Strategic decisions are high-level choices that shape the long-term direction and goals of an organization. These decisions typically involve top-level executives and have a significant impact on the entire organization. Strategic decisions often revolve around aspects such as market positioning, resource allocation, mergers and acquisitions, entering new markets, and developing new products or services. They require extensive analysis, consideration of market trends, competitive landscape, and long-term implications.
Tactical Decision Making:
Tactical decisions are more specific and focus on implementing the broader strategic decisions within a particular department or functional area of the organization. These decisions are made by middle-level managers or department heads to achieve short to medium-term objectives. Tactical decisions may include resource allocation within departments, process improvements, workforce planning, pricing strategies, marketing campaigns, and supplier selection. They require a balance between strategic alignment and operational feasibility.
Operational Decision Making:
Operational decisions are routine choices made by front-line managers or employees to ensure smooth day-to-day operations of the organization. These decisions are typically repetitive in nature and aim to address immediate operational issues or tasks within established guidelines or standard operating procedures (SOPs). Examples of operational decisions include inventory management, scheduling shifts, customer service responses, quality control measures, equipment maintenance scheduling, and order fulfillment processes.
It is important to note that these decision-making types are interconnected and interdependent. Strategic decisions set the overall direction for an organization; tactical decisions implement those strategies; while operational decisions ensure the execution of plans at a granular level. Effective decision-making at all levels is crucial for achieving organizational goals and maintaining competitiveness in today’s dynamic business environment.