The Decision-Making Process in Operations Management: A Guide to Effective Choices
In the field of operations management, making sound decisions is crucial for the success and efficiency of any organization. Whether it’s selecting suppliers, optimizing production processes, or managing inventory levels, every decision has a direct impact on the overall performance and profitability.
The decision-making process in operations management involves a systematic approach that ensures informed choices are made based on relevant data and analysis. Let’s explore the key steps involved in this process:
Identifying the Problem or Opportunity:
The first step is to clearly define the problem or opportunity that requires a decision. This could be anything from improving production efficiency to reducing costs or responding to changes in customer demand. It’s important to have a clear understanding of the objective before proceeding further.
Gathering Information:
Once the problem is identified, gather all relevant information related to it. This includes data on current processes, market trends, competitor analysis, customer feedback, and any other factors that may influence the decision-making process. The more comprehensive and accurate the information, the better-informed decisions can be made.
Generating Alternatives:
Brainstorming multiple alternatives is essential for expanding the range of possible solutions. Encourage creativity and involve key stakeholders from different departments or teams within the organization. Each alternative should be evaluated based on its feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and alignment with organizational goals.
Evaluating Alternatives:
This step involves analyzing each alternative against predetermined criteria such as cost, quality, time constraints, resource availability, and risk factors. Quantitative techniques like cost-benefit analysis or decision matrix models can be employed to compare options objectively.
Selecting an Option:
After evaluating each alternative thoroughly, it’s time to select the most suitable option. Consider both short-term gains and long-term implications while making this choice. It may also be beneficial to seek input from subject matter experts or consult with other stakeholders to ensure a well-rounded perspective.
Implementing the Decision:
Once the decision is made, it’s time to put it into action. Develop an implementation plan that outlines the necessary steps, assigns responsibilities, and sets realistic timelines. Effective communication and coordination among teams are essential during this phase to ensure a smooth transition.
Monitoring and Evaluating:
After implementing the decision, closely monitor its impact on operations. Regularly assess whether the expected outcomes are being achieved and make adjustments if necessary. Collect feedback from employees, track performance metrics, and compare results against the predetermined criteria to evaluate the effectiveness of the decision.
Learning from Experience:
Every decision provides an opportunity for learning and improvement. Conduct post-decision reviews to identify strengths, weaknesses, and lessons learned from the process. Documenting these insights can help refine future decision-making practices and enhance organizational performance over time.
In conclusion, effective decision making in operations management requires a systematic approach that considers all relevant factors. By following a structured process like the one outlined above, organizations can make informed choices that optimize operations, improve efficiency, and drive overall success. Remember, decisions shape the future of your organization – so choose wisely!
Frequently Asked Questions: Decision-Making Process in Operations Management
- What are the 5 steps in the decision-making process?
- What are 4 types of decision-making process?
- What are the 8 steps in decision-making process in management?
- What is decision-making in operations management?
What are the 5 steps in the decision-making process?
The decision-making process typically involves five key steps:
- Identify the Problem or Opportunity: The first step is to clearly define the problem or recognize the opportunity that requires a decision. This involves understanding the current situation, identifying any challenges or issues, and determining the desired outcome.
- Gather Information: Once the problem or opportunity is identified, gather all relevant information related to it. This includes collecting data, conducting research, seeking input from stakeholders, and considering different perspectives. The goal is to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the situation and gather sufficient information to make an informed decision.
- Evaluate Alternatives: Generate a range of possible solutions or alternatives that could address the problem or capitalize on the opportunity. Evaluate each alternative by assessing its feasibility, potential outcomes, risks involved, and alignment with organizational goals and values. This step may involve using various decision-making tools such as cost-benefit analysis, SWOT analysis, or decision matrices.
- Make a Decision: After evaluating the alternatives, select the most suitable option based on the information gathered and analysis conducted in previous steps. Consider both short-term and long-term implications of each alternative before making a final decision. It may be helpful to consult with relevant stakeholders or subject matter experts during this process.
- Implement and Evaluate: Once a decision is made, put it into action by developing an implementation plan. Assign responsibilities, allocate necessary resources, and establish timelines for execution. Monitor the implementation closely to ensure it aligns with the intended outcome. Regularly evaluate progress against predetermined criteria and make adjustments if needed.
It’s important to note that these steps are not always linear and can involve iterations or modifications based on new information or changing circumstances throughout the process. Effective decision making requires careful consideration of available options while balancing analytical thinking with intuition and experience.
What are 4 types of decision-making process?
There are several types of decision-making processes that individuals and organizations can employ, depending on the nature of the decision and the context in which it is being made. Here are four common types:
Rational Decision Making:
Rational decision making is a systematic and logical approach that involves gathering relevant information, evaluating alternatives, and selecting the most optimal choice based on quantitative analysis. This process aims to maximize outcomes while minimizing risks and uncertainties. It is often used for complex decisions that require careful consideration of multiple factors.
Intuitive Decision Making:
Intuitive decision making relies on gut feelings, instincts, and past experiences to make choices without extensive analysis or deliberation. This approach is often used when time is limited or when dealing with familiar situations where individuals can rely on their expertise and intuition to make quick decisions.
Incremental Decision Making:
Incremental decision making involves making small adjustments or changes over time rather than making significant or radical choices at once. This approach allows for flexibility and adaptability while continuously refining decisions based on feedback and learning from previous actions. It is commonly used in situations where uncertainty is high or when there are multiple viable options.
Group Decision Making:
Group decision making involves involving multiple individuals or stakeholders in the decision-making process. This can be done through brainstorming sessions, discussions, or formal meetings where ideas are shared, debated, and evaluated collectively. Group decision making leverages diverse perspectives, expertise, and collaboration to reach a consensus or make a democratic choice.
It’s important to note that these types of decision-making processes are not mutually exclusive, and they can be combined or adapted based on the specific circumstances of each decision-making situation. The key is to select an approach that aligns with the complexity of the problem at hand, the available resources, and the desired outcome.
What are the 8 steps in decision-making process in management?
The decision-making process in management typically involves the following eight steps:
- Identifying the Problem or Opportunity: Clearly define the issue that requires a decision. This step involves recognizing a problem or identifying an opportunity for improvement.
- Gathering Information: Collect all relevant data and information related to the problem or opportunity. This includes analyzing internal and external factors, conducting research, and seeking input from stakeholders.
- Analyzing the Situation: Evaluate the gathered information to gain a comprehensive understanding of the situation. Identify patterns, trends, and potential causes of the problem or opportunities for improvement.
- Generating Alternatives: Brainstorm multiple possible solutions or courses of action to address the problem or capitalize on the opportunity. Encourage creativity and involve key stakeholders in this process.
- Evaluating Alternatives: Assess each alternative against predetermined criteria such as feasibility, cost-effectiveness, impact on resources, risks involved, and alignment with organizational goals. Use quantitative techniques like cost-benefit analysis or decision matrix models to compare options objectively.
- Selecting an Option: Based on the evaluation of alternatives, choose the most suitable option that best addresses the problem or maximizes potential benefits. Consider short-term gains as well as long-term implications while making this choice.
- Implementing the Decision: Develop a detailed plan for executing the selected option. Assign responsibilities, set realistic timelines, and ensure effective communication and coordination among teams involved in implementing the decision.
- Monitoring and Evaluating: Regularly monitor and evaluate the progress of implementing the decision. Collect feedback from stakeholders, track performance metrics, and compare results against predetermined criteria to assess whether desired outcomes are being achieved.
It’s important to note that decision-making is an iterative process, meaning that steps may need to be revisited if new information arises or if adjustments are required based on ongoing evaluation.
By following these eight steps systematically, managers can make informed decisions that align with organizational goals and drive success.
What is decision-making in operations management?
Decision-making in operations management refers to the process of selecting the best course of action among various alternatives to achieve operational goals and improve overall performance within an organization. It involves analyzing data, evaluating options, and making informed choices that impact the design, planning, control, and improvement of operations.
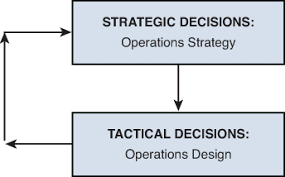
In operations management, decisions are made at different levels, ranging from strategic decisions that shape the long-term direction of the organization’s operations to tactical decisions that focus on specific areas such as production planning or inventory management. These decisions are critical for ensuring efficient utilization of resources, meeting customer demands, optimizing processes, and ultimately enhancing competitiveness.
The decision-making process in operations management typically involves identifying problems or opportunities, gathering relevant information, generating alternative solutions, evaluating those alternatives based on predefined criteria, selecting the most suitable option, implementing the decision effectively, monitoring its outcomes, and learning from the experience for future improvements.
Operations managers often rely on quantitative techniques such as forecasting models, optimization algorithms, statistical analysis tools, and simulation methods to support their decision-making process. These tools help analyze data and provide insights into factors like demand patterns, resource allocation strategies, capacity planning scenarios, supply chain optimization possibilities, quality control measures, and more.
Effective decision-making in operations management requires a combination of analytical skills to interpret data accurately and managerial judgment to consider various trade-offs. It also involves collaboration with cross-functional teams and stakeholders to ensure alignment with organizational objectives.
By making well-informed decisions in operations management, organizations can enhance efficiency and productivity while reducing costs and risks. It enables them to streamline processes effectively, improve customer satisfaction levels through timely delivery and quality products or services while maintaining a competitive advantage in today’s dynamic business environment.