Strategic Management and Decision Making: Navigating the Path to Success
In today’s fast-paced and highly competitive business landscape, strategic management and decision making play a crucial role in an organization’s success. The ability to make sound decisions while aligning them with long-term goals is what sets successful companies apart from the rest. Let’s delve into the world of strategic management and decision making, exploring their importance and how they go hand in hand.
Strategic management involves the formulation and implementation of plans, initiatives, and actions that enable organizations to achieve their objectives. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including setting goals, analyzing internal and external environments, formulating strategies, allocating resources effectively, and monitoring progress. It is a continuous process that requires adaptability and agility to navigate through ever-changing market dynamics.
At the heart of strategic management lies decision making. Decisions are at the core of every action taken within an organization. Whether it’s deciding on new product development, entering new markets, or allocating resources, decisions shape the direction of an organization. Effective decision making involves gathering relevant information, analyzing alternatives, evaluating risks, considering potential outcomes, and selecting the best course of action.
Strategic management provides a framework for decision making by aligning decisions with an organization’s mission, vision, values, and long-term goals. It helps leaders make informed choices that not only address current challenges but also position the organization for future success. By adopting a strategic mindset when making decisions, leaders can ensure that their actions are consistent with the overall strategy.
One key aspect of strategic management is understanding the external environment in which an organization operates. This includes assessing industry trends, competitor analysis, market dynamics, regulatory factors, technological advancements, and customer preferences. By gaining insights into these external factors through thorough analysis and research, organizations can make informed decisions that capitalize on opportunities while mitigating risks.
Internal analysis is equally vital in strategic decision making. Leaders must evaluate the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, resources, capabilities, and core competencies. This self-assessment helps identify areas where the organization has a competitive advantage and areas that require improvement. By leveraging internal strengths and addressing weaknesses, organizations can make decisions that align with their unique value proposition.
Strategic management also emphasizes the importance of collaboration and involvement from stakeholders at all levels. By involving employees, customers, suppliers, and other key stakeholders in the decision-making process, organizations can gain different perspectives and insights. This participatory approach not only enhances decision quality but also fosters a sense of ownership and commitment among stakeholders.
In conclusion, strategic management and decision making are intertwined disciplines that drive organizational success. They provide a roadmap for navigating through complex business environments while ensuring that decisions are aligned with long-term goals. By adopting a strategic mindset when making decisions and leveraging comprehensive analysis of internal and external factors, organizations can position themselves for sustainable growth and competitive advantage. Embracing strategic management principles empowers leaders to make informed choices that shape the future of their organizations.
Common Questions About Strategic Management and Decision Making: Explained
- How does strategic management help in decision making?
- What is the relationship between management and decision making?
- What is decision making strategies in management?
- What is decision making models in strategic management?
How does strategic management help in decision making?
Strategic management plays a crucial role in decision making by providing a framework and guiding principles that help leaders make informed choices aligned with the organization’s long-term goals. Here are some ways in which strategic management helps in decision making:
- Alignment with Goals: Strategic management ensures that decisions are consistent with the organization’s mission, vision, values, and strategic objectives. It provides a clear direction and purpose, enabling leaders to make decisions that contribute to the overall strategic direction of the organization.
- Long-term Perspective: Strategic management encourages a long-term perspective when making decisions. It considers not only immediate outcomes but also their potential impact on future success. By considering long-term consequences, leaders can avoid short-sighted decisions that may hinder progress down the line.
- Risk Assessment: Strategic management emphasizes the importance of assessing risks associated with different decision options. It encourages leaders to evaluate potential risks and rewards, enabling them to make calculated decisions that balance risk and return. This proactive approach helps organizations anticipate challenges and take appropriate measures to mitigate risks.
- Resource Allocation: Effective resource allocation is critical for organizational success. Strategic management helps leaders prioritize resources by identifying areas of strategic importance and allocating them accordingly. By aligning resource allocation with strategic priorities, organizations can optimize their use of limited resources.
- Environmental Analysis: Strategic management involves analyzing both internal and external environments before making decisions. This analysis provides valuable insights into market trends, competitor behavior, technological advancements, regulatory factors, customer preferences, and other relevant factors. By considering these factors during decision making, organizations can adapt to changing circumstances and capitalize on opportunities.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Strategic management promotes stakeholder involvement in decision-making processes. By seeking input from employees, customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders, organizations gain diverse perspectives and insights that enhance decision quality. Involving stakeholders also fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the decisions made.
- Evaluation and Adaptation: Strategic management emphasizes the importance of monitoring and evaluating decisions’ outcomes. By regularly assessing the impact of decisions, organizations can identify what worked well and what needs improvement. This feedback loop enables continuous learning and adaptation, enhancing future decision-making processes.
In summary, strategic management provides a structured approach to decision making by aligning choices with long-term goals, considering risks and rewards, analyzing the internal and external environment, involving stakeholders, and evaluating outcomes. By incorporating strategic management principles into decision making, organizations can make informed choices that support their overall strategy and drive sustainable success.
What is the relationship between management and decision making?
Management and decision making are closely interconnected and interdependent. Decision making is a fundamental aspect of management, as managers are responsible for making decisions that guide the organization towards its goals and objectives.
Management involves planning, organizing, leading, and controlling various resources within an organization to achieve desired outcomes. Decision making is an essential component of the planning function of management, as it involves selecting the most appropriate course of action from available alternatives to achieve specific objectives.
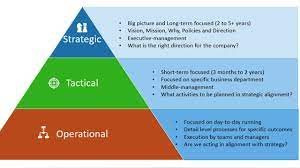
Managers make decisions at different levels within an organization. Strategic decisions are made by top-level managers and involve long-term planning and goal setting. Tactical decisions are made by middle-level managers and focus on implementing strategies and allocating resources effectively. Operational decisions are made by lower-level managers and deal with day-to-day activities to ensure smooth operations.
Effective decision making requires managers to gather relevant information, analyze alternatives, consider potential risks and outcomes, evaluate trade-offs, and select the best course of action. Managers must also consider various internal and external factors that may impact their decisions, such as market conditions, organizational capabilities, resource availability, customer needs, legal requirements, and competitive pressures.
Management provides a framework for decision making by establishing goals, objectives, policies, procedures, and guidelines that guide the decision-making process. It provides a structured approach to decision making by defining roles and responsibilities within the organization.
On the other hand, decision making influences management by shaping the direction of an organization. Decisions determine resource allocation, budgeting priorities, staffing requirements, technology investments, product development strategies, market entry or exit decisions, and more. Effective decision making enables managers to align their actions with organizational goals while adapting to changing circumstances.
Furthermore, management involves not only individual decision making but also collective decision-making processes involving teams or groups within an organization. Collaboration among managers in decision-making processes can lead to better outcomes through diverse perspectives and expertise.
In summary, management encompasses various functions aimed at achieving organizational goals while decision making is an integral part of management. Managers rely on effective decision making to plan, organize, lead, and control resources within an organization. The relationship between management and decision making is symbiotic, as management provides a framework for decision making, while decision making shapes management by guiding actions and influencing outcomes.
What is decision making strategies in management?
Decision-making strategies in management refer to the approaches and methodologies used by managers to make effective and informed decisions. These strategies are designed to guide managers in analyzing situations, evaluating alternatives, and selecting the most appropriate course of action. Here are some common decision-making strategies used in management:
- Rational Decision Making: This strategy involves a systematic and logical approach to decision making. It includes identifying the problem, gathering relevant information, evaluating alternatives based on predetermined criteria, selecting the best option, and implementing it. Rational decision making aims to maximize outcomes by considering all available information.
- Intuitive Decision Making: Intuition-based decision making relies on the manager’s experience, expertise, and gut feeling. It involves quickly assessing a situation based on past experiences and making a decision without extensive analysis. Intuitive decisions can be effective when time is limited or when faced with familiar situations.
- Incremental Decision Making: This strategy involves making decisions incrementally by taking small steps rather than pursuing a comprehensive solution all at once. It allows for flexibility and adjustment as new information becomes available or circumstances change over time.
- Consensus Decision Making: In this approach, managers seek input from team members or stakeholders to reach a collective agreement. The goal is to ensure that everyone’s opinions and perspectives are considered before making a decision. Consensus decision making promotes collaboration, engagement, and ownership among team members.
- Risk-based Decision Making: This strategy involves assessing potential risks associated with each alternative before making a decision. Managers consider the probability of success or failure, potential consequences, and potential mitigation measures to minimize risks.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Cost-benefit analysis is a quantitative approach that compares the costs of different alternatives against their expected benefits or outcomes. It helps managers evaluate options based on their economic impact and determine which alternative provides the greatest net benefit.
- Data-driven Decision Making: Data-driven decision making relies on analyzing relevant data and information to inform the decision-making process. Managers collect and analyze data, such as market trends, customer feedback, financial reports, and performance metrics, to make informed decisions based on objective evidence.
- Ethical Decision Making: This strategy involves considering ethical principles and values when making decisions. Managers assess the potential impact of their decisions on stakeholders, society, and the organization’s reputation. Ethical decision making ensures that decisions align with moral standards and social responsibility.
It’s important for managers to select the most appropriate decision-making strategy based on the nature of the problem, available information, time constraints, and organizational context. Employing effective decision-making strategies can enhance managerial effectiveness and contribute to overall organizational success.
What is decision making models in strategic management?
Decision-making models in strategic management are frameworks or approaches that guide the process of making decisions within an organization. These models provide a structured and systematic way to analyze information, evaluate alternatives, and select the best course of action. Here are a few common decision-making models used in strategic management:
- Rational Decision-Making Model: This model assumes that decision makers are rational and seek to maximize outcomes by carefully evaluating all available information, generating alternatives, weighing their pros and cons, and selecting the option with the highest expected value. It follows a logical sequence of steps, including problem identification, information gathering, alternative generation, evaluation, selection, and implementation.
- Bounded Rationality Model: In contrast to the rational model, this model recognizes that decision makers have limitations in processing information due to time constraints or cognitive biases. It suggests that individuals make decisions that are “good enough” rather than optimal. Decision makers satisfice by selecting the first acceptable option that meets their criteria rather than exhaustively analyzing all alternatives.
- Incremental Decision-Making Model: This model acknowledges that decisions are often made incrementally over time rather than in one big leap. It suggests that organizations make small adjustments and improvements based on feedback and learning from previous decisions. This approach allows for flexibility and adaptation as new information becomes available.
- Political Decision-Making Model: This model recognizes that organizational decision making is influenced by power struggles, conflicts of interest, and differing perspectives among stakeholders. It emphasizes the importance of negotiation, coalition-building, and compromise to reach decisions that satisfy multiple stakeholders’ interests.
- Intuitive Decision-Making Model: Intuition plays a significant role in decision making when there is limited time or incomplete information available. This model relies on individuals’ expertise and experience to make quick judgments based on patterns or cues without explicit analysis.
It’s important to note that these models are not mutually exclusive but can be combined or adapted based on the specific context and complexity of the decision at hand. Strategic management often involves a blend of these models, considering both rational analysis and intuitive judgment to make effective decisions that align with the organization’s goals and objectives.