Strategic Management: The Art of Decision Making
In the complex and ever-evolving world of business, strategic management plays a pivotal role in the success and growth of organizations. It is an ongoing process that involves making critical decisions to steer a company towards its long-term objectives. At its core, strategic management is the art of decision making, encompassing a range of activities designed to maximize an organization’s competitive advantage.
The process of strategic management begins with setting clear goals and objectives. These goals serve as guideposts, providing direction and purpose for the organization. They help define the desired outcomes and provide a framework for decision making.
Once goals are established, the next step in strategic management is conducting a thorough analysis of both internal and external factors that may impact the organization’s ability to achieve those goals. This analysis includes evaluating market trends, assessing competitors, understanding customer needs, and assessing the internal capabilities and resources of the organization.
Based on this analysis, strategic managers identify strategic options or alternatives that align with the organization’s goals. These options may involve expanding into new markets, developing new products or services, or improving operational efficiency. Each option is carefully evaluated based on its potential risks, rewards, and alignment with the overall strategy.
Decision making in strategic management requires weighing different alternatives against each other and selecting the most suitable course of action. It involves considering various factors such as financial implications, resource allocation, market dynamics, and organizational capabilities. Effective decision making requires a combination of analytical thinking, creativity, intuition, and experience.
Once decisions are made, they need to be translated into actionable plans. This involves developing detailed strategies that outline specific actions to be taken to achieve the desired outcomes. These plans provide a roadmap for implementation and serve as a basis for monitoring progress towards achieving strategic goals.
However, strategic management is not a one-time event; it is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adaptation. Markets change rapidly, technologies evolve, and customer preferences shift. Therefore, strategic managers must regularly review and reassess their strategies to ensure they remain relevant and effective in a dynamic business environment.
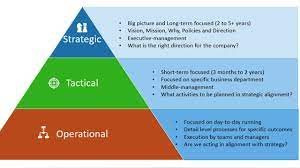
Strategic management is not limited to large corporations or multinational companies. It is equally important for small businesses, startups, nonprofits, and even individuals. Regardless of the size or nature of the organization, strategic decision making helps create a clear vision, aligns resources effectively, and maximizes the chances of success.
In conclusion, strategic management is the process of decision making that guides organizations towards their long-term goals. It involves setting objectives, analyzing internal and external factors, identifying alternatives, making informed decisions, developing actionable plans, and continuously monitoring progress. By embracing strategic management principles, organizations can navigate the complexities of today’s business landscape with confidence and achieve sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions about Strategic Management and Decision-Making
- What are the two processes of strategic management?
- What is the role of strategic management in decision-making?
- What are the 3 process of strategic management?
- What is the strategic decision-making process?
What are the two processes of strategic management?
The two key processes of strategic management are formulation and implementation.
1. Formulation: This process involves the development of a clear and comprehensive strategy for the organization. It includes analyzing the internal and external environment, setting goals and objectives, identifying strategic alternatives, and making informed decisions about the best course of action. During formulation, strategic managers assess factors such as market trends, competitive landscape, customer needs, resources, and capabilities to develop a strategic plan that aligns with the organization’s vision.
2. Implementation: Once the strategy is formulated, the implementation process begins. This stage focuses on translating the strategic plan into action by effectively allocating resources, assigning responsibilities, and executing specific initiatives. Implementation requires strong leadership, effective communication, coordination among different departments or teams, and monitoring progress towards achieving strategic goals. It involves making sure that the necessary actions are taken to bring the strategy to life and drive organizational performance.
These two processes of strategic management are interconnected and iterative. Formulation provides the foundation for implementation, while implementation informs refinements in formulation based on feedback and results. Effective integration of both processes is essential for organizations to successfully execute their strategies and adapt to changing circumstances in order to achieve long-term success.
What is the role of strategic management in decision-making?
Strategic management plays a crucial role in decision-making within an organization. It provides a structured approach and framework for making informed and effective decisions that align with the organization’s long-term goals and objectives. Here are some key roles of strategic management in decision-making:
- Setting Direction: Strategic management helps define the direction and purpose of an organization by setting clear goals and objectives. These goals serve as a guide for decision-making, ensuring that all decisions are aligned with the overall strategy.
- Analyzing Internal and External Factors: Strategic management involves conducting a thorough analysis of internal strengths, weaknesses, resources, capabilities, as well as external market trends, competitors, customer needs, and industry dynamics. This analysis provides valuable insights that inform decision-making processes.
- Identifying Alternatives: Based on the analysis conducted, strategic management helps identify various strategic alternatives or options that can be pursued to achieve the desired outcomes. These alternatives are evaluated based on their alignment with the strategy and their potential impact on organizational success.
- Evaluating Risks and Rewards: Strategic management considers both the risks and rewards associated with each alternative. It involves assessing potential risks such as financial implications, resource allocation challenges, market uncertainties, competitive threats, and regulatory factors. By evaluating these factors, strategic managers can make informed decisions that balance risk-taking with potential rewards.
- Decision-Making Process: Strategic management provides a structured decision-making process that takes into account various factors such as financial considerations, resource allocation requirements, market dynamics, competitive positioning, and organizational capabilities. It helps ensure that decisions are well-thought-out and based on reliable information.
- Developing Actionable Plans: Once decisions are made, strategic management translates them into actionable plans by outlining specific steps to be taken to implement the chosen strategies effectively. These plans provide a roadmap for execution and help allocate resources efficiently.
- Monitoring Progress: Strategic management also plays a role in monitoring progress towards achieving strategic goals. It involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), measuring outcomes, and making adjustments as needed. This monitoring process ensures that decisions remain effective and relevant in a dynamic business environment.
In summary, strategic management provides a structured approach to decision-making by setting direction, analyzing internal and external factors, identifying alternatives, evaluating risks and rewards, developing actionable plans, and monitoring progress. It helps organizations make informed decisions that are aligned with their long-term objectives and maximize their chances of success.
What are the 3 process of strategic management?
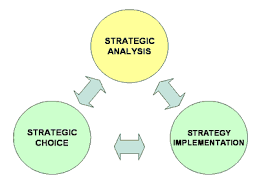
The strategic management process typically consists of three main stages:
- Strategy Formulation: This initial stage involves the development of a clear and comprehensive strategy. It begins with setting the organization’s mission, vision, and objectives. The process then moves on to conducting an analysis of the internal and external environment, including factors such as industry trends, market dynamics, competitive landscape, and organizational capabilities. Based on this analysis, strategic options or alternatives are identified and evaluated. This stage culminates in the selection of a strategy that best aligns with the organization’s goals and resources.
- Strategy Implementation: Once a strategy is formulated, it needs to be translated into action. This stage focuses on effectively implementing the chosen strategy throughout the organization. It involves developing detailed plans, allocating resources appropriately, setting targets and milestones, and assigning responsibilities to individuals or teams. Effective communication and coordination are crucial during this stage to ensure that everyone understands their roles and works together towards achieving strategic objectives.
- Strategy Evaluation: The final stage of strategic management involves monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the implemented strategy. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are established to measure progress towards strategic goals. Regular assessments are conducted to determine if the strategy is yielding desired outcomes or if adjustments need to be made. Feedback loops are established to gather insights from various stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners. Based on evaluation results, strategic managers can make informed decisions about refining or adapting the strategy as needed.
It is important to note that strategic management is an iterative process rather than a linear one. The three stages described above often overlap and interact with each other continuously as new information becomes available or circumstances change. Flexibility and adaptability are key in ensuring that organizations remain agile in response to evolving market conditions while staying focused on their long-term objectives.
What is the strategic decision-making process?
The strategic decision-making process is a systematic approach used by organizations to make important decisions that impact their long-term goals and overall direction. While the specific steps may vary depending on the organization, industry, or context, the general strategic decision-making process typically includes the following stages:
- Setting Objectives: The process begins with clearly defining the organization’s objectives and desired outcomes. These objectives provide a clear vision of what the organization aims to achieve and serve as a foundation for decision making.
- Environmental Analysis: This stage involves conducting a comprehensive analysis of both internal and external factors that may influence the organization’s ability to achieve its objectives. Internal analysis examines strengths, weaknesses, resources, and capabilities within the organization, while external analysis focuses on market trends, competition, regulatory factors, and customer needs.
- Generating Alternatives: Based on the environmental analysis, decision makers identify various strategic alternatives or options that could help achieve the desired objectives. This stage encourages creative thinking and brainstorming to come up with diverse possibilities.
- Evaluating Alternatives: In this stage, decision makers critically evaluate each alternative against specific criteria such as feasibility, alignment with organizational goals, potential risks and rewards, financial implications, resource requirements, and market dynamics. This evaluation helps narrow down the options to those most likely to lead to success.
- Making Decisions: After careful evaluation of alternatives, decision makers select one or a combination of options that best align with organizational goals and constraints. The final decision may involve trade-offs and compromises based on available resources and priorities.
- Developing Action Plans: Once decisions are made, action plans are developed to outline specific steps required for implementation. Action plans break down strategic decisions into actionable tasks with clear responsibilities, timelines, resource allocation requirements, and performance indicators.
- Implementation: This stage involves executing the action plans according to the established timelines and monitoring progress closely. Effective communication within the organization is crucial during this phase to ensure understanding, commitment, and coordination among relevant stakeholders.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular monitoring and evaluation of the implemented strategies are essential to assess their effectiveness and make any necessary adjustments. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are established to measure progress towards objectives, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions for continuous improvement.
- Feedback and Learning: Throughout the strategic decision-making process, organizations should encourage feedback from stakeholders, employees, customers, and other relevant parties. This feedback helps in identifying areas for improvement and learning from past experiences to enhance future decision making.
It is important to note that the strategic decision-making process is not necessarily linear or sequential. It often involves iteration and adaptation as new information becomes available or circumstances change. Flexibility, agility, and continuous learning are vital for effective strategic decision making in today’s dynamic business environment.