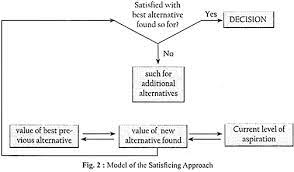
Understanding Decision Making Theory
Decision making is a crucial aspect of everyday life, influencing both personal and professional outcomes. Decision making theory seeks to explain how individuals make choices when faced with multiple options or alternatives.
One prominent theory in decision making is the rational decision-making model. According to this model, individuals make decisions by systematically evaluating all available options, considering the consequences of each choice, and selecting the option that maximizes their utility or satisfaction.
Another important theory is bounded rationality, which suggests that individuals do not always have the time or cognitive resources to make fully rational decisions. Instead, they rely on heuristics or mental shortcuts to simplify the decision-making process.
Prospect theory is another influential theory in decision making, proposing that individuals tend to weigh potential losses more heavily than gains when making decisions under uncertainty. This can lead to risk-averse behavior in certain situations.
Understanding decision making theory can help individuals improve their decision-making skills and make more informed choices. By recognizing the factors that influence decision making, such as cognitive biases and emotional influences, individuals can learn to make better decisions that align with their goals and values.
Five Key Benefits of Decision Making Theory: Frameworks, Objectivity, Insights, Bias Identification, and Empowered Choices
- Provides a framework for understanding how individuals make choices
- Helps individuals evaluate and compare different options objectively
- Offers insights into the factors that influence decision making processes
- Aids in identifying cognitive biases and heuristics that may impact decisions
- Empowers individuals to make more informed and strategic decisions
Seven Critiques of Decision Making Theory: Oversimplification, Emotional Oversight, and Practical Challenges
- Decision making theory can oversimplify complex decision-making processes.
- It may not fully account for the emotional and psychological factors that influence decisions.
- Some decision making theories assume individuals always act rationally, which may not reflect real-life behavior.
- Theoretical models may not consider cultural or individual differences in decision-making styles.
- Decision making theory does not always address the impact of external influences on choices.
- It may be challenging to apply theoretical concepts to practical decision-making situations.
- Overreliance on decision making theory could lead to a lack of creativity and flexibility in problem-solving.
Provides a framework for understanding how individuals make choices
Decision making theory provides a valuable framework for understanding how individuals make choices. By exploring various models and theories of decision making, we can gain insights into the factors that influence our decision-making processes. This framework helps us analyze the cognitive processes, biases, and heuristics that shape our choices. Understanding these underlying mechanisms enables us to make more deliberate and informed decisions in both personal and professional contexts. Ultimately, by grasping how individuals navigate through options and evaluate alternatives, decision making theory offers a structured approach to comprehending the complexities of human decision making.
Helps individuals evaluate and compare different options objectively
One significant advantage of decision making theory is its ability to assist individuals in evaluating and comparing different options objectively. By providing a structured framework for decision making, this aspect of the theory encourages individuals to consider all available alternatives based on relevant criteria and factors. This systematic approach helps in minimizing biases and subjective influences, enabling individuals to make more rational and informed choices that align with their goals and objectives. Ultimately, the emphasis on objectivity in decision making theory promotes a thorough analysis of options, leading to more effective decision outcomes.
Offers insights into the factors that influence decision making processes
One significant advantage of decision making theory is its ability to offer valuable insights into the various factors that influence decision-making processes. By studying and understanding these factors, such as cognitive biases, emotions, environmental influences, and personal values, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of how decisions are made. This knowledge empowers individuals to recognize and account for these influences when making choices, ultimately leading to more informed and effective decision-making outcomes.
Aids in identifying cognitive biases and heuristics that may impact decisions
One significant advantage of decision making theory is its ability to aid in identifying cognitive biases and heuristics that may impact decisions. By understanding these inherent mental shortcuts and biases, individuals can become more aware of how they influence their decision-making process. This awareness allows individuals to take steps to mitigate the effects of these biases, leading to more rational and informed decision-making outcomes.
Empowers individuals to make more informed and strategic decisions
Decision making theory empowers individuals to make more informed and strategic decisions by providing a structured framework for evaluating options, considering potential outcomes, and weighing the risks and benefits of each choice. By understanding the principles of decision making theory, individuals can enhance their ability to analyze situations objectively, identify the most favorable course of action, and make decisions that align with their goals and values. This enables individuals to approach decision making with greater confidence and clarity, leading to more effective and successful outcomes in both personal and professional contexts.
Decision making theory can oversimplify complex decision-making processes.
Decision making theory, while providing valuable frameworks for understanding how decisions are made, can sometimes oversimplify complex decision-making processes. By focusing on idealized models of rational decision making, these theories may fail to account for the myriad factors that can influence real-world decisions. In practice, decision making is often messy and involves ambiguity, uncertainty, and emotional considerations that cannot always be neatly captured by theoretical models. This oversimplification can lead to a disconnect between theory and reality, potentially limiting the effectiveness of decision-making strategies in complex and dynamic situations.
It may not fully account for the emotional and psychological factors that influence decisions.
One significant drawback of decision making theory is its limitation in fully accounting for the emotional and psychological factors that play a crucial role in influencing decisions. While traditional decision-making models emphasize rationality and logic, they often overlook the impact of emotions, biases, and psychological states on the decision-making process. Emotions such as fear, excitement, or stress can significantly sway decision outcomes, leading individuals to make choices that may not align with their best interests or long-term goals. Ignoring these emotional and psychological factors can result in suboptimal decisions that fail to consider the holistic nature of human decision making.
Some decision making theories assume individuals always act rationally, which may not reflect real-life behavior.
Some decision making theories have a notable con in that they assume individuals always act rationally, which may not accurately reflect real-life behavior. In reality, people are often influenced by emotions, biases, and external factors that can lead to decisions that deviate from purely rational choices. This limitation in decision making theory highlights the complexity of human decision-making processes and the need to consider a broader range of factors beyond strict rationality when analyzing and understanding how decisions are made in practice.
Theoretical models may not consider cultural or individual differences in decision-making styles.
One significant con of decision making theory is that theoretical models often overlook cultural or individual differences in decision-making styles. These models may assume a universal approach to decision making, failing to account for the diverse values, beliefs, and preferences that shape how individuals from different cultures or backgrounds make choices. Cultural norms, personal experiences, and social influences can all play a significant role in shaping an individual’s decision-making process. Ignoring these factors in theoretical models can lead to oversimplified or inaccurate representations of real-world decision making, potentially limiting the applicability and effectiveness of such theories in diverse contexts.
Decision making theory does not always address the impact of external influences on choices.
One significant drawback of decision making theory is its limited consideration of external influences on choices. Decision making models often overlook the impact of external factors such as societal norms, cultural beliefs, peer pressure, and environmental conditions on an individual’s decision-making process. These external influences can significantly affect the choices individuals make, yet traditional decision making theories tend to focus more on internal cognitive processes rather than the broader context in which decisions are made. Ignoring these external influences can lead to a narrow understanding of decision making and may result in suboptimal or biased choices.
It may be challenging to apply theoretical concepts to practical decision-making situations.
One significant con of decision making theory is that it may be challenging to apply theoretical concepts to practical decision-making situations. While decision making theories provide valuable frameworks and insights into the decision-making process, translating these theoretical concepts into real-world scenarios can be complex. Practical decision-making situations often involve various complexities, uncertainties, and unique factors that may not neatly align with the assumptions or structures of decision making theories. This disconnect between theory and practice can make it difficult for individuals to effectively utilize theoretical models when making decisions in their everyday lives or professional environments.
Overreliance on decision making theory could lead to a lack of creativity and flexibility in problem-solving.
An inherent con of decision making theory is the risk of overreliance, which can potentially stifle creativity and limit flexibility in problem-solving approaches. By strictly adhering to established decision-making models and techniques, individuals may overlook unconventional or innovative solutions that could lead to more effective outcomes. This overreliance on decision making theory may hinder the ability to adapt to unique or complex situations that require thinking outside the traditional framework. Embracing a balance between structured decision-making principles and creative problem-solving strategies is essential to ensure a comprehensive approach to decision making that considers all possibilities and fosters innovation.