Decision Making in Project Management: Key Strategies for Success
Effective decision making is crucial in project management as it directly impacts the success or failure of a project. The ability to make sound decisions amidst complexity, uncertainty, and time constraints is a skill that every project manager should possess. In this article, we will explore key strategies for making informed decisions in project management.
- Define Clear Objectives: Before making any decision, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the project’s objectives. Clearly define what you aim to achieve, what the desired outcomes are, and how they align with the overall goals of the organization. This clarity will act as a guiding principle when faced with decision-making dilemmas.
- Gather Relevant Information: Making well-informed decisions requires gathering and analyzing relevant data and information. Ensure that you have access to accurate and up-to-date information related to the project at hand. Consult subject matter experts, conduct research, and utilize reliable sources to gather all the necessary facts before proceeding.
- Identify Alternatives: It is important to explore different options or alternatives when making decisions in project management. Consider various approaches, strategies, or solutions that could address the challenges or opportunities at hand. Evaluate each alternative based on its feasibility, potential risks, resource requirements, and impact on project objectives.
- Assess Risks and Benefits: Every decision involves an element of risk. Evaluate potential risks associated with each alternative and assess their potential impact on the project’s success. Similarly, consider the benefits or advantages that each option offers in terms of achieving project objectives. Balancing risks against benefits is crucial for effective decision making.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engaging stakeholders throughout the decision-making process can lead to more successful outcomes. Seek input from relevant team members, clients, sponsors, or other stakeholders who may have valuable insights or expertise related to specific aspects of the project. Their perspectives can provide a broader understanding of potential consequences and help identify blind spots.
- Consider Constraints: Project management often operates within constraints such as time, budget, and resources. When making decisions, it is important to consider these constraints and their impact on the available options. Assess whether the decision aligns with project limitations or if adjustments need to be made to accommodate the constraints.
- Evaluate Long-Term Implications: Decisions made in project management should not only focus on short-term gains but also consider long-term implications. Assess how each decision may impact future stages of the project, as well as its alignment with broader organizational goals or strategies. Taking a holistic view can prevent potential conflicts or setbacks down the line.
- Monitor and Adapt: Decision making is an ongoing process in project management. Continuously monitor the outcomes of your decisions and be prepared to adapt if necessary. Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your decisions and make adjustments based on feedback, changing circumstances, or new information that may arise during project execution.
In conclusion, effective decision making is a critical skill for project managers. By following these key strategies – defining clear objectives, gathering relevant information, identifying alternatives, assessing risks and benefits, involving stakeholders, considering constraints, evaluating long-term implications, and monitoring outcomes – project managers can enhance their ability to make informed decisions that drive successful project outcomes.
Demystifying Decision Making in Project Management: 4 Frequently Asked Questions
- What are 5 steps of decision making?
- What are the 7 steps of decision making?
- What are the 4 types of decision making?
- Why is decision making important in projects?
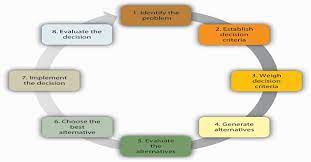
What are 5 steps of decision making?
The decision-making process typically involves several steps. While there are various models and frameworks available, here are five common steps that can guide the decision-making process:
- Identify and Define the Problem: The first step is to clearly identify and define the problem or the decision that needs to be made. This involves understanding the context, gathering relevant information, and determining the desired outcome.
- Generate Alternatives: Once the problem is defined, brainstorm and generate a range of possible alternatives or solutions. Encourage creativity and consider different perspectives to explore all potential options.
- Evaluate Alternatives: Assess each alternative by considering its pros and cons, feasibility, potential risks, resource requirements, and alignment with goals or values. Use analytical tools or decision matrices if necessary to compare and prioritize alternatives.
- Make a Decision: Based on the evaluation of alternatives, make a decision by selecting the option that best aligns with your objectives and has the highest likelihood of success. Consider both rational analysis and intuition in making your final choice.
- Implement and Review: After making a decision, it is essential to put it into action effectively. Develop an action plan, allocate resources, assign responsibilities, and monitor progress throughout implementation. Additionally, regularly review the outcomes of your decision to learn from successes or failures and adjust strategies as needed.
Remember that decision making is not always a linear process; it often involves iterations or revisiting previous steps based on new information or changing circumstances. Flexibility in adapting your decisions can contribute to better outcomes in dynamic environments.
What are the 7 steps of decision making?
The 7 steps of decision making are as follows:
- Identify the Decision: The first step is to clearly identify the decision that needs to be made. This involves understanding the problem or opportunity that requires a decision and defining its scope.
- Gather Information: Once the decision is identified, gather all relevant information related to the situation. This includes collecting data, facts, opinions, and insights that will help in understanding the various aspects of the decision.
- Identify Alternatives: Generate a list of possible alternatives or options that could potentially address the problem or capitalize on the opportunity. Consider different approaches, strategies, or solutions that could be considered.
- Evaluate Alternatives: Assess each alternative by considering its pros and cons, potential risks and benefits, feasibility, and alignment with goals and values. Use criteria such as cost-effectiveness, impact on stakeholders, time constraints, and resource availability to evaluate each option.
- Make a Decision: Based on the evaluation of alternatives, select the best option that aligns with your objectives and provides the most favorable outcome. Be prepared to make trade-offs if necessary.
- Take Action: Once a decision is made, take action to implement it effectively. Develop an action plan outlining specific steps, responsibilities, timelines, and resources required for successful execution.
- Evaluate Results: After implementing the decision, evaluate its results and outcomes. Assess whether it achieved the desired objectives and if any adjustments or improvements are needed for future decisions in similar situations.
It’s important to note that these steps can be iterative in nature; you may need to revisit certain stages based on new information or changing circumstances throughout the decision-making process.
What are the 4 types of decision making?
There are several models and frameworks that categorize decision-making types. One commonly referenced model is the following:
- Routine Decision Making: This type of decision making involves repetitive and straightforward choices that are made on a regular basis with little or no conscious thought. These decisions are typically based on established rules, policies, or standard operating procedures.
- Tactical Decision Making: Tactical decisions are made in response to specific situations or problems that require analysis and evaluation. They often involve a higher level of complexity and require a more deliberate approach than routine decisions. Tactical decisions are typically made by mid-level managers or project teams to address operational issues.
- Strategic Decision Making: Strategic decisions are high-stakes choices that have a significant impact on an organization’s long-term goals and direction. These decisions involve assessing risks, analyzing market trends, considering competitive advantages, and evaluating potential outcomes. Strategic decisions are typically made by top-level executives or business owners.
- Crisis Decision Making: Crisis decisions occur in urgent or emergency situations where immediate action is required to mitigate potential harm or address unforeseen circumstances. These decisions are often made under high-pressure conditions with limited time for analysis and consideration of alternatives.
It is important to note that decision-making processes can vary depending on the context, industry, organizational structure, and individual preferences. Different models may identify additional types of decision making or classify them differently. Nonetheless, understanding these four general categories provides a useful framework for discussing decision-making approaches in various contexts.
Why is decision making important in projects?
Decision making is vital in projects for several reasons:
- Project Direction: Decision making helps establish the direction and focus of a project. It determines the goals, objectives, and strategies that will guide the project’s execution. Without clear decision making, projects can lack purpose and fail to achieve their intended outcomes.
- Resource Allocation: Projects typically have limited resources, including time, budget, and manpower. Effective decision making ensures these resources are allocated wisely to maximize efficiency and productivity. Decisions help prioritize tasks, allocate budgets, assign responsibilities, and manage resources effectively throughout the project lifecycle.
- Risk Management: Projects inherently involve risks and uncertainties. Decision making plays a crucial role in identifying potential risks, evaluating their impact on project success, and developing strategies to mitigate or manage them. By making informed decisions based on risk analysis, project managers can minimize potential threats and increase the chances of project success.
- Problem Solving: Projects often encounter unexpected challenges or obstacles that require quick thinking and problem-solving skills. Decision making enables project managers to assess situations objectively, identify alternative solutions or approaches, weigh pros and cons, and select the most appropriate course of action to address problems effectively.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Projects involve multiple stakeholders with diverse interests and perspectives. Effective decision making involves engaging stakeholders throughout the process to ensure their needs are considered and addressed appropriately. By involving stakeholders in decision-making processes, projects can build consensus, foster collaboration, enhance communication, and increase stakeholder satisfaction.
- Adaptability: Projects operate within dynamic environments where changes are inevitable. Decision making allows project managers to adapt quickly in response to changing circumstances or new information that may arise during project execution. It enables them to make timely adjustments to plans or strategies without compromising project objectives.
- Learning from Experience: Decision making provides an opportunity for continuous learning in projects. By evaluating the outcomes of decisions made in previous projects or phases, project managers can gain insights into what worked well and what didn’t. This knowledge can be leveraged to make better-informed decisions in future projects, improving overall project performance and outcomes.
In summary, decision making is essential in projects as it establishes project direction, optimizes resource allocation, manages risks, solves problems, engages stakeholders, enables adaptability, and facilitates continuous learning. Effective decision making enhances project outcomes and increases the likelihood of project success.