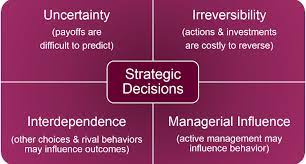
Decision Making Techniques in Project Management
Effective decision making is a critical skill for project managers. In the fast-paced and complex world of project management, decisions need to be made quickly and accurately to ensure successful outcomes. To achieve this, project managers rely on various decision-making techniques that help them navigate through uncertainties and make informed choices. In this article, we will explore some popular decision-making techniques used in project management.
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This technique involves identifying and analyzing these four elements to assess the current situation of a project. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of the project, as well as potential opportunities and threats, project managers can make decisions that leverage strengths, mitigate weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and address threats.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: This technique involves evaluating the costs associated with a decision against its potential benefits. Project managers assess both tangible and intangible costs and benefits to determine if a proposed action will generate enough value to justify its implementation. This analysis helps prioritize options based on their expected return on investment (ROI) or other relevant criteria.
- Decision Trees: Decision trees are visual tools that help project managers analyze multiple possible outcomes of a decision by mapping out different paths or scenarios. Each scenario is assigned probabilities based on their likelihood of occurring. By considering the potential outcomes and their probabilities, project managers can evaluate which decision path is most favorable.
- Pareto Analysis: The Pareto principle states that roughly 80% of problems come from 20% of causes. In project management, Pareto analysis involves identifying the most significant issues or factors impacting a project’s success by focusing on those that contribute the most to problems or delays. By addressing these critical factors first, project managers can allocate resources effectively and make decisions that have the greatest impact on overall performance.
- Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA): MCDA is a technique that helps project managers evaluate and compare multiple options based on various criteria or factors. Each criterion is assigned a weight to reflect its relative importance. By systematically assessing each option against the criteria and applying the weights, project managers can make decisions that align with project objectives and stakeholder priorities.
- Decision Matrix: A decision matrix, also known as a decision-making grid, is a tool that helps project managers evaluate different alternatives against specific criteria. By assigning scores or rankings to each option based on how well they meet the criteria, project managers can objectively compare and select the most suitable alternative.
- Brainstorming: Brainstorming is a widely used technique for generating creative solutions or ideas. Project managers gather team members or stakeholders in a collaborative session to generate as many ideas as possible without judgment or criticism. This technique encourages diverse perspectives and can lead to innovative solutions that may not have been considered otherwise.
These are just a few of the many decision-making techniques available to project managers. Each technique has its own strengths and areas of applicability, so it’s essential for project managers to select the appropriate technique based on the specific context and nature of their projects.
By employing these decision-making techniques, project managers can enhance their ability to make informed choices, minimize risks, and ultimately drive successful project outcomes. Effective decision making is an invaluable skill in project management, enabling teams to navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and deliver projects that meet stakeholder expectations.
Answering Your Top 5 Questions on Decision Making Techniques in Project Management
- What decision making techniques should I use in project management?
- How do I make decisions effectively in project management?
- What are the best practices for decision making in project management?
- How can I ensure that my decisions are sound in project management?
- What tools and resources are available to help with decision making in project management?
What decision making techniques should I use in project management?
In project management, the choice of decision-making techniques depends on various factors such as the complexity of the project, the available information, the level of uncertainty, and the preferences of the project team. Here are a few commonly used decision-making techniques that you can consider:
- SWOT Analysis: Conduct a SWOT analysis to assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with your project. This technique helps you understand the current situation and make decisions that leverage strengths, address weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate threats.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Evaluate the costs and benefits associated with different options or decisions. By comparing both tangible and intangible costs against potential benefits, you can prioritize alternatives based on their expected return on investment (ROI) or other relevant criteria.
- Decision Trees: Use decision trees to map out different paths or scenarios based on possible outcomes and their probabilities. This technique helps you visualize potential consequences and make decisions based on calculated risks.
- Pareto Analysis: Apply the Pareto principle to identify critical factors or issues that contribute most to problems or delays in your project. By addressing these high-impact factors first, you can prioritize resources effectively and make decisions that have a significant impact on overall performance.
- Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA): If you have multiple options to consider, use MCDA to evaluate them against various criteria or factors. Assign weights to each criterion to reflect its relative importance and systematically assess each option’s alignment with project objectives and stakeholder priorities.
- Decision Matrix: Create a decision matrix or grid to compare different alternatives against specific criteria. Assign scores or rankings based on how well each option meets those criteria. This technique provides an objective way to compare options and select the most suitable alternative.
- Brainstorming: Engage your team members or stakeholders in brainstorming sessions to generate creative ideas or solutions for complex problems or decisions. Encourage open and diverse thinking without judgment to foster innovation and gather valuable input.
Remember, the choice of decision-making techniques should be based on the unique characteristics of your project and the specific decisions you need to make. It’s also essential to involve relevant stakeholders and consider their perspectives when applying these techniques.
How do I make decisions effectively in project management?
Making decisions effectively in project management requires a systematic and thoughtful approach. Here are some key steps to help you make informed and successful decisions:
- Define the Decision: Clearly identify the decision that needs to be made. Understand the problem or opportunity at hand, and establish the desired outcome or objective.
- Gather Information: Collect all relevant data and information related to the decision. This may involve conducting research, analyzing project documents, consulting stakeholders, or seeking expert opinions. Ensure that you have a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing the decision.
- Identify Alternatives: Generate a range of possible options or solutions to address the decision at hand. Encourage brainstorming sessions with your team or stakeholders to explore different perspectives and ideas. Consider both traditional and innovative alternatives.
- Evaluate Options: Assess each alternative against predetermined criteria or factors that are important for your project’s success. Consider factors such as feasibility, cost, risk, impact on project objectives, stakeholder requirements, and resource availability. Use decision-making techniques like cost-benefit analysis, SWOT analysis, or decision matrices to objectively evaluate each option.
- Analyze Risks and Uncertainties: Consider potential risks and uncertainties associated with each alternative. Evaluate their potential impact on project outcomes and determine strategies to mitigate or manage them effectively.
- Seek Input from Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders in the decision-making process by seeking their input and feedback. Engage in open communication to understand their perspectives, concerns, and expectations regarding the decision.
- Make a Decision: Based on your evaluation of alternatives and stakeholder input, make a well-informed decision that aligns with project goals and objectives. Choose an option that offers the best balance between benefits, risks, resources, and stakeholder needs.
- Communicate Your Decision: Clearly communicate your decision to all relevant stakeholders involved in the project. Provide rationale behind your choice and address any concerns they may have. Ensure that everyone understands the decision and its implications.
- Implement and Monitor: Develop an action plan to implement the decision effectively. Assign responsibilities, allocate resources, and establish timelines. Regularly monitor and evaluate the progress of the decision’s implementation to ensure it is on track and achieving desired outcomes.
- Learn and Adapt: Project management is an iterative process, and decisions may need to be adjusted or revised based on changing circumstances or new information. Continuously evaluate the impact of your decision and be open to adapting if necessary.
By following these steps, project managers can enhance their decision-making process, minimize risks, and increase the likelihood of successful project outcomes. Remember that effective decision making requires a balance between analysis, stakeholder engagement, and sound judgment based on experience and expertise.
What are the best practices for decision making in project management?
When it comes to decision making in project management, there are several best practices that can help ensure successful outcomes. Here are some key practices to consider:
- Clearly Define the Decision: Before making any decision, it’s crucial to clearly define the problem or situation that needs to be addressed. This involves understanding the objectives, constraints, and desired outcomes associated with the decision.
- Gather Relevant Information: To make informed decisions, gather all relevant information related to the problem at hand. This may involve conducting research, seeking input from subject matter experts, analyzing data, and considering historical project information.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders who have a vested interest in the decision-making process. By involving those affected by or accountable for the decision, you can gain valuable insights and perspectives that can lead to better choices and increased buy-in.
- Evaluate Alternatives: Identify and evaluate multiple alternatives or options before making a final decision. Consider the advantages, disadvantages, risks, and potential impacts of each alternative on project objectives and stakeholder expectations.
- Assess Risks: Assess the risks associated with each alternative and consider their potential impact on project success. Implement risk mitigation strategies as necessary to manage uncertainties effectively.
- Use Decision-Making Techniques: Apply appropriate decision-making techniques (such as SWOT analysis, cost-benefit analysis, or decision trees) based on the complexity of the problem and available resources. These techniques can provide structure and objectivity to the decision-making process.
- Consider Long-Term Implications: Look beyond immediate outcomes and consider the long-term implications of your decisions on future project phases or related initiatives. Anticipate potential consequences and align your choices with broader organizational goals.
- Communicate Effectively: Transparent communication is vital throughout the decision-making process. Clearly articulate your rationale behind decisions made, share relevant information with stakeholders, listen actively to their concerns or feedback, and address any questions or uncertainties promptly.
- Document Decisions: Keep a record of all decisions made, along with the reasons behind them. This documentation serves as a reference point and helps maintain accountability throughout the project lifecycle.
- Learn from Experience: Continuously evaluate the outcomes and impact of your decisions. Reflect on lessons learned and incorporate them into future decision-making processes to improve decision quality and project performance over time.
By following these best practices, project managers can enhance their decision-making capabilities, minimize risks, and increase the likelihood of successful project outcomes. Remember that effective decision making is an ongoing process that requires adaptability, collaboration, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
How can I ensure that my decisions are sound in project management?
Ensuring sound decisions in project management requires a systematic approach and careful consideration of various factors. Here are some key steps you can take to enhance the soundness of your decisions:
- Gather Relevant Information: Before making any decision, gather all the necessary information related to the project, including objectives, constraints, risks, and available resources. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of the project’s context and requirements.
- Identify Stakeholders: Identify and involve key stakeholders who will be affected by or have an interest in the decision-making process. Consider their perspectives, needs, and expectations when evaluating options.
- Define Decision Criteria: Clearly define the criteria that will guide your decision-making process. These criteria should align with project goals and stakeholder requirements. Common criteria include cost, quality, time, feasibility, impact on stakeholders, and risk.
- Evaluate Alternatives: Generate a range of alternatives or options to address the decision at hand. Assess each alternative against the defined criteria to determine their strengths, weaknesses, potential risks, benefits, and impacts.
- Seek Expert Opinions: Consult subject matter experts or experienced individuals who can provide valuable insights into specific aspects of the decision-making process. Their expertise can help you make more informed choices.
- Analyze Risks: Consider potential risks associated with each alternative and evaluate their likelihood and potential impact on project objectives. Mitigate or manage these risks as much as possible before making a final decision.
- Use Decision-Making Techniques: Apply appropriate decision-making techniques such as SWOT analysis, cost-benefit analysis, decision trees, or multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) to evaluate alternatives objectively and systematically.
- Test Assumptions: Identify any assumptions underlying your decision-making process and test them for validity by gathering additional data or seeking expert opinions if needed.
- Consider Long-Term Implications: Assess how each alternative aligns with long-term project goals, sustainability, and the potential for future scalability or adaptability.
- Document and Communicate: Document the decision-making process, including the rationale behind your chosen alternative. Communicate the decision clearly to all relevant stakeholders, ensuring that they understand the reasoning and implications.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor the outcomes of your decisions and evaluate their effectiveness. If necessary, be open to adjusting or revising decisions based on new information or changing circumstances.
Remember that no decision-making process is foolproof, but by following these steps, you can increase the likelihood of making sound decisions in project management. Regularly reflecting on your decision-making approach and seeking feedback from team members can also help you refine your skills over time.
What tools and resources are available to help with decision making in project management?
In project management, there are numerous tools and resources available to support decision-making processes. Here are some commonly used ones:
- Project Management Software: Project management software platforms, such as Microsoft Project, Asana, Trello, and Jira, offer features that assist with decision making. These tools provide a centralized platform for tracking project progress, managing tasks, collaborating with team members, and generating reports. They often include features like Gantt charts, task dependencies, and customizable dashboards that aid in making informed decisions based on real-time project data.
- Decision Support Systems (DSS): DSS are computer-based tools that help analyze complex problems and support decision making. These systems utilize data analysis techniques and mathematical models to provide insights into different scenarios or alternatives. DSS can assist project managers in evaluating risks, predicting outcomes, and selecting the most suitable course of action.
- Data Analytics Tools: Analytical tools like Microsoft Excel or specialized data analytics software can be invaluable for decision making in project management. These tools allow project managers to organize and analyze large amounts of data to identify patterns, trends, and potential risks. By leveraging data analytics capabilities, project managers can make data-driven decisions that are grounded in objective analysis.
- Risk Management Tools: Risk management is an integral part of decision making in project management. Risk assessment tools like the Risk Probability-Impact Matrix (also known as the Risk Matrix) or Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) help identify potential risks associated with specific decisions or actions. These tools enable project managers to prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact on the project’s objectives.
- Decision Templates: Decision templates provide a structured framework for evaluating options and making decisions based on predefined criteria. Templates can include elements such as cost-benefit analysis sheets, decision matrices, or SWOT analysis frameworks. These templates streamline the decision-making process by ensuring consistency and facilitating the consideration of relevant factors.
- Lessons Learned Databases: Lessons learned databases or knowledge repositories store information from past projects, including decisions made and their outcomes. These resources allow project managers to access historical data and insights to inform current decision-making processes. By learning from previous experiences, project managers can avoid repeating mistakes and leverage successful strategies.
- Expert Networks and Communities: Engaging with professional networks, online communities, or industry-specific forums can provide project managers with valuable insights and advice from experienced professionals. These networks offer opportunities for knowledge sharing, peer-to-peer learning, and seeking guidance on complex decisions.
- Training and Professional Development: Ongoing training programs, workshops, certifications, and seminars in project management equip professionals with decision-making skills. These educational resources provide frameworks, methodologies, and best practices that enhance decision-making capabilities in various project scenarios.
Remember that the selection of tools and resources should align with the specific needs of your projects and organization. It’s essential to evaluate their suitability based on factors like project complexity, team size, budget constraints, and available expertise.