Title: Evidence-Based Decision Making: A Practical Example
Introduction:
In today’s complex and fast-paced world, making decisions can be a challenging task. However, by adopting evidence-based decision making (EBDM), individuals and organizations can enhance their ability to make informed choices based on reliable data and rigorous analysis. In this article, we will explore a practical example of how evidence-based decision making can be applied in real-life situations.
The Example: Improving Customer Satisfaction in a Retail Business
Let’s consider a retail business that has been experiencing declining customer satisfaction ratings. The management team recognizes the importance of addressing this issue promptly and decides to utilize an evidence-based approach to identify the root causes and develop effective solutions.
Identifying the Problem:
The first step is to clearly define the problem. In this case, it is declining customer satisfaction ratings. The management team gathers available data, such as customer feedback surveys, online reviews, and sales records, to gain insights into the specific areas of concern.
Gathering Evidence:
To make informed decisions, the team collects additional evidence related to customer satisfaction. They conduct interviews with customers, hold focus groups, and analyze competitor benchmarks. This comprehensive approach ensures that they have a holistic understanding of the situation.
Analyzing Data:
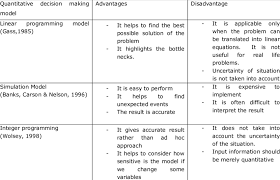
With an abundance of data at hand, the team employs statistical analysis techniques to identify patterns and trends within the information gathered. They use tools like regression analysis or correlation studies to determine which factors are most strongly associated with declining customer satisfaction.
Developing Solutions:
Based on their analysis, the team identifies several potential factors contributing to low customer satisfaction—for instance, long waiting times at checkout counters or unhelpful staff interactions. They prioritize these factors based on their impact and feasibility for improvement.
Testing Solutions:
Rather than implementing all potential solutions at once, the team selects one or two interventions to test on a smaller scale—a pilot program or limited-time trial. This allows them to evaluate the effectiveness of each solution and make adjustments before rolling out changes across the entire organization.
Monitoring and Evaluation:
Throughout the implementation process, the team monitors key performance indicators related to customer satisfaction, such as survey results, sales data, and customer complaints. They compare these metrics against pre-intervention benchmarks to assess the impact of their evidence-based decisions.
Continuous Improvement:
EBDM is an ongoing process. The retail business continually collects feedback from customers, monitors market trends, and adjusts strategies accordingly. By remaining open to new evidence and adapting their decision-making approach, they can consistently improve customer satisfaction over time.
Conclusion:
This practical example demonstrates how evidence-based decision making can be applied to address complex challenges effectively. By collecting and analyzing relevant data, organizations can make informed choices that lead to positive outcomes. Whether it’s improving customer satisfaction or solving other complex problems, embracing an evidence-based approach empowers individuals and organizations with the tools needed for success in today’s dynamic world.
8 Tips for Effective Evidence-Based Decision Making
- Gather evidence from multiple sources
- Analyse the evidence objectively
- Consider potential risks and benefits of each decision
- Verify accuracy of data
- Use quantitative analysis when possible
- Develop a hypothesis
- Test your hypothesis
- Document your findings
Gather evidence from multiple sources
Gather evidence from multiple sources: A Key Tip for Evidence-Based Decision Making
When it comes to making informed decisions, relying on a single source of information may not provide a comprehensive and accurate understanding of the situation. That’s why gathering evidence from multiple sources is a crucial tip for effective evidence-based decision making.
In today’s information age, we have access to an abundance of data and resources. By tapping into various sources, we can gather a diverse range of perspectives, insights, and facts that contribute to a more well-rounded decision-making process.
By gathering evidence from multiple sources, we can:
Obtain a broader perspective: Different sources offer different viewpoints and experiences. By considering various perspectives, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the issue at hand. This helps us avoid biases and make more informed decisions.
Validate information: Not all information is created equal. By cross-referencing data from different sources, we can verify its accuracy and reliability. This helps us avoid basing decisions on potentially flawed or biased information.
Identify patterns and trends: When we analyze data from multiple sources, patterns and trends may emerge that would otherwise go unnoticed if we relied on only one source. These patterns can provide valuable insights that inform our decision-making process.
Mitigate risks: Relying solely on one source of information increases the risk of overlooking critical factors or potential pitfalls. Gathering evidence from multiple sources allows us to identify potential risks and make more robust decisions that account for various scenarios.
So how can we gather evidence from multiple sources effectively? Here are a few practical steps:
Diversify your research: Look beyond just one type of source or method when collecting data. Consider academic research papers, industry reports, expert opinions, case studies, surveys, interviews, or even personal experiences.
Evaluate credibility: Assess the credibility and reliability of each source before incorporating it into your decision-making process. Consider factors such as the source’s expertise, reputation, methodology, and potential biases.
Seek diverse perspectives: Engage with a wide range of stakeholders who have different backgrounds and viewpoints. This can include colleagues, experts, customers, or even members of the community who are directly impacted by the decision.
Synthesize information: Once you have gathered evidence from multiple sources, synthesize the information to identify common themes, discrepancies, or areas requiring further investigation. This synthesis will help you make sense of the diverse data and form a comprehensive understanding.
By following this tip of gathering evidence from multiple sources, you can enhance your decision-making process and increase the likelihood of making well-informed choices that yield positive outcomes.
Remember: in a world where information is abundant but not always reliable, diversifying your sources of evidence is key to making evidence-based decisions that stand the test of time.
Analyse the evidence objectively
Title: Analyzing Evidence Objectively: A Key Element of Evidence-Based Decision Making
Introduction:
When it comes to evidence-based decision making, one crucial aspect that cannot be overlooked is the objective analysis of the evidence at hand. By approaching data and information without bias or preconceived notions, individuals and organizations can make more accurate and reliable decisions. In this article, we will explore the importance of analyzing evidence objectively in the context of evidence-based decision making.
Unveiling Bias:
Human beings are naturally prone to biases that can influence their judgment. These biases can stem from personal beliefs, past experiences, or even societal influences. However, when engaging in evidence-based decision making, it is essential to recognize and set aside these biases to ensure an objective analysis of the evidence.
The Role of Objectivity:
Analyzing evidence objectively means approaching it with an open mind and a willingness to consider all relevant information without favoring any particular outcome. It involves critically evaluating the quality, reliability, and relevance of the evidence before drawing conclusions or making decisions.
Key Steps for Objective Analysis:
To analyze evidence objectively, consider following these steps:
Define Clear Evaluation Criteria: Establish a set of criteria against which you will assess the quality and reliability of the evidence. This helps maintain consistency and ensures that subjective opinions do not overshadow factual information.
Seek Diverse Perspectives: Encourage input from multiple sources or stakeholders who may have different viewpoints or expertise related to the issue at hand. This helps prevent confirmation bias and provides a more comprehensive understanding of the situation.
Apply Critical Thinking: Scrutinize the evidence by asking critical questions such as: Is there sufficient data? Are there any conflicting findings? Are there any limitations or potential sources of bias in the research methodology? This helps identify potential weaknesses or gaps in the evidence.
Consider Contradictory Evidence: Be open to contradictory findings or perspectives that challenge your initial assumptions. Evaluating conflicting evidence can provide a more balanced view and lead to more robust decision making.
Consult Experts: When dealing with complex or technical subjects, consult experts in the field who possess specialized knowledge and expertise. Their insights can help you interpret the evidence accurately and make informed decisions.
Benefits of Objective Analysis:
By analyzing evidence objectively, you can reap several benefits:
Enhanced Decision Making: Objectivity allows for a more accurate assessment of the evidence, leading to better-informed decisions that are less influenced by personal biases or subjective opinions.
Increased Credibility: Objective analysis lends credibility to your decision-making process, as it demonstrates a commitment to basing decisions on reliable information rather than personal preferences or biases.
Improved Outcomes: By relying on objective analysis, you increase the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes, as decisions are grounded in solid evidence rather than assumptions or unsupported claims.
Conclusion:
Analyzing evidence objectively is a fundamental principle of evidence-based decision making. By setting aside biases and approaching information with an open mind, individuals and organizations can make better-informed choices that lead to more successful outcomes. Embracing objectivity in the analysis of evidence is key to unlocking the full potential of evidence-based decision making in various aspects of life and work.
Consider potential risks and benefits of each decision
When it comes to making decisions, especially important ones, it is crucial to consider the potential risks and benefits associated with each option. This is a key principle of evidence-based decision making (EBDM) that helps individuals and organizations make well-informed choices based on a thorough understanding of the potential outcomes.
By carefully weighing the risks and benefits, decision makers can assess the potential impact of their choices and make decisions that align with their goals and values. Here’s why considering these factors is so important:
- Minimizing Risks: Every decision carries some level of risk. By evaluating the potential risks associated with each option, you can identify any potential pitfalls or negative consequences that may arise. This allows you to take proactive measures to mitigate those risks or develop contingency plans to handle them effectively.
- Maximizing Benefits: On the flip side, considering the benefits helps you identify the positive outcomes that may result from a particular decision. By understanding the potential advantages, you can prioritize options that align with your objectives and maximize the desired benefits.
- Balancing Trade-offs: Decision making often involves trade-offs where certain choices come with both advantages and disadvantages. By carefully assessing these trade-offs, you can weigh whether the benefits outweigh the risks or vice versa. This enables you to make more informed decisions that strike a balance between different factors.
- Long-term Impact: Considering both risks and benefits helps in evaluating not only immediate consequences but also long-term effects. It allows you to think beyond short-term gains or losses and consider how each decision may impact your future goals, sustainability, or overall well-being.
- Ethical Considerations: Assessing risks and benefits also plays a role in ethical decision making. It ensures that decisions are made in alignment with ethical principles by considering factors such as fairness, justice, integrity, and respect for stakeholders’ rights.
Incorporating risk and benefit analysis into your decision-making process may involve gathering relevant data, consulting experts or stakeholders, and conducting thorough research. It’s important to critically evaluate the information available and consider multiple perspectives to make a well-rounded assessment.
Remember, evidence-based decision making is about making informed choices based on reliable data and rigorous analysis. By considering the potential risks and benefits of each decision, you can increase your chances of making decisions that lead to positive outcomes while minimizing undesirable consequences.
Verify accuracy of data
Title: The Key to Informed Decision Making: Verify Accuracy of Data
Introduction:
In the realm of evidence-based decision making, accurate data is the foundation upon which sound choices are built. Without reliable information, decisions can be misguided and potentially lead to unfavorable outcomes. Therefore, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of verifying the accuracy of data before making any significant decisions. In this article, we will explore why data verification is a critical step and how it contributes to effective evidence-based decision making.
The Significance of Data Accuracy:
Data serves as the backbone of evidence-based decision making. It provides insights into trends, patterns, and correlations that help us understand complex situations and make informed choices. However, not all data is created equal. Inaccurate or unreliable data can skew our understanding and misguide our decisions.
The Consequences of Relying on Inaccurate Data:
Depending on inaccurate data can have severe consequences. It may lead to flawed analysis, faulty predictions, and ultimately poor decision making. Organizations may waste valuable resources pursuing ineffective strategies or miss out on opportunities due to a distorted understanding of the situation at hand.
Steps for Verifying Data Accuracy:
- Source Evaluation: Begin by assessing the credibility and reputation of the source providing the data. Consider factors such as expertise, transparency, and previous track record in delivering accurate information.
- Cross-Referencing: Compare data from multiple sources to identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies. When different sources align on a particular point, it increases confidence in its accuracy.
- Fact-Checking: Conduct thorough fact-checking by verifying specific details against trusted references or experts in the field. This step helps weed out inaccuracies that might have slipped through initial evaluations.
- Data Collection Methods: Scrutinize how the data was collected and ensure that proper methodologies were employed during the process. Understanding how the information was gathered helps assess its reliability.
- Data Integrity Checks: Utilize data integrity checks to identify any anomalies or errors within the dataset. This can involve running validation tests, checking for missing values, or examining outliers that may indicate potential issues.
- Peer Review: Seek feedback and input from colleagues or subject matter experts to validate the accuracy of the data. An external perspective can help identify blind spots or uncover potential biases.
Conclusion:
Verifying the accuracy of data is an essential step in evidence-based decision making. By ensuring that our information is reliable and trustworthy, we can make informed choices that lead to desired outcomes. Through source evaluation, cross-referencing, fact-checking, and other verification methods, we can confidently rely on accurate data to guide our decision-making processes. Remember, accurate data empowers us with the knowledge needed to navigate complex challenges successfully and make informed choices that drive positive results.
Use quantitative analysis when possible
Tip: Use Quantitative Analysis When Possible for Evidence-Based Decision Making
When it comes to evidence-based decision making, one valuable tip is to utilize quantitative analysis whenever possible. Quantitative analysis involves the use of numerical data and statistical methods to derive insights and make informed decisions. This approach offers several advantages that can enhance the accuracy and reliability of your decision-making process.
Quantitative analysis provides objectivity by removing personal biases and subjective interpretations. By relying on data-driven evidence, you can avoid making decisions based solely on opinions or assumptions. Instead, you can rely on concrete numbers and facts to guide your choices.
Another benefit of quantitative analysis is its ability to provide a clear understanding of trends, patterns, and correlations within the data. By employing statistical techniques, you can identify relationships between variables, determine cause-and-effect relationships, and predict future outcomes with a certain level of confidence.
Furthermore, quantitative analysis allows for precise measurement and comparison. It enables you to quantify the impact or significance of different factors or options under consideration. This allows decision makers to prioritize actions based on their potential impact or return on investment.
In addition, quantitative analysis facilitates effective communication and collaboration within teams or organizations. Numbers provide a common language that everyone can understand, making it easier to share insights, discuss findings, and reach consensus when making decisions collectively.
However, it’s important to note that quantitative analysis may not always be feasible or appropriate for every situation. Some decisions may involve qualitative factors that cannot be easily quantified. In such cases, a combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches might be needed for a more comprehensive understanding.
To effectively use quantitative analysis in evidence-based decision making:
- Clearly define your research question or problem statement.
- Identify the relevant variables that need measurement.
- Collect reliable data from credible sources.
- Analyze the data using appropriate statistical techniques.
- Interpret the results objectively while considering any limitations.
- Make informed decisions based on the evidence generated.
Remember, quantitative analysis is just one tool in the evidence-based decision-making toolbox. It should be used in conjunction with other methods, such as qualitative analysis and expert opinions, to ensure a well-rounded and comprehensive decision-making process.
By incorporating quantitative analysis into your evidence-based decision-making approach, you can harness the power of data to make more informed choices, minimize risks, and achieve better outcomes.
Develop a hypothesis
Developing a Hypothesis: A Key Step in Evidence-Based Decision Making
When it comes to evidence-based decision making, developing a hypothesis plays a crucial role in guiding the entire process. A hypothesis is essentially an educated guess or prediction about the relationship between variables or factors that are relevant to the decision at hand. By formulating a clear and testable hypothesis, individuals and organizations can streamline their decision-making process and increase the chances of making informed choices.
The purpose of developing a hypothesis is to provide a framework for gathering evidence and conducting further analysis. It helps focus efforts on specific variables or factors that are believed to have an impact on the desired outcome. Let’s consider an example to illustrate how developing a hypothesis can contribute to evidence-based decision making:
Scenario: A company is experiencing declining sales in one of its product lines.
Hypothesis: The company hypothesizes that the decline in sales is due to increased competition from similar products offered by competitors.
In this example, the hypothesis suggests that competition is the main factor influencing declining sales. With this hypothesis in mind, the company can now gather evidence to either support or refute it. They might collect market research data, analyze competitor strategies, conduct customer surveys, or review sales figures from previous years.
By focusing their efforts on testing this specific hypothesis, the company can avoid getting overwhelmed by irrelevant information and concentrate on gathering evidence related to competition. This approach allows them to make more targeted decisions based on concrete findings.
It’s important to note that developing a hypothesis doesn’t mean assuming it as absolute truth from the start. Instead, it serves as an initial guiding principle that will be tested through further analysis and evaluation of evidence. If new evidence emerges during the process that challenges the initial hypothesis, adjustments can be made accordingly.
In summary, developing a hypothesis is a critical step in evidence-based decision making. It provides direction for collecting relevant data and helps narrow down potential variables or factors that may influence the decision. By formulating a clear hypothesis and systematically testing it, individuals and organizations can make more informed choices based on reliable evidence, ultimately increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Test your hypothesis
One crucial step in evidence-based decision making is testing your hypothesis. When faced with a problem or a decision to make, it’s important to develop a hypothesis—a proposed explanation or solution based on available evidence. However, it’s equally important to subject that hypothesis to testing before making a final decision.
Testing your hypothesis allows you to gather additional data and evaluate the viability of your proposed solution. It helps you understand whether your initial assumptions are accurate and whether the chosen course of action will yield the desired results.
To effectively test your hypothesis, consider the following steps:
- Define clear criteria: Clearly outline what success or failure looks like for your hypothesis. Establish measurable goals and indicators that can objectively determine whether your solution is effective.
- Design experiments or trials: Develop a plan to test your hypothesis in a controlled manner. This could involve conducting surveys, running pilot programs, or implementing small-scale experiments.
- Collect data: Gather relevant data during the testing phase. This may include surveys, observations, interviews, or any other method that provides insights into the impact of your proposed solution.
- Analyze results: Carefully analyze the collected data to determine if it supports or contradicts your initial hypothesis. Look for patterns, trends, and statistical significance that can guide your decision-making process.
- Adjust and refine: Based on the results of testing, be open to adjusting and refining your initial hypothesis as needed. If the data suggests that alternative solutions may be more effective, consider adapting your approach accordingly.
Testing hypotheses brings objectivity into decision making by relying on empirical evidence rather than relying solely on intuition or assumptions. It minimizes risks associated with making decisions based solely on untested ideas.
Remember that evidence-based decision making is an iterative process; it involves continuously gathering new information and refining hypotheses as you progress towards optimal solutions. By incorporating testing into your decision-making framework, you increase the likelihood of making well-informed choices that lead to positive outcomes.
In summary, testing your hypothesis is a critical step in evidence-based decision making. It allows you to validate your assumptions, gather additional data, and refine your proposed solutions. By embracing this practice, you can make more informed decisions that are grounded in evidence and increase the chances of achieving desired results.
Document your findings
One crucial tip in evidence-based decision making is to document your findings. When engaging in the process of gathering and analyzing data, it is essential to keep a thorough record of your discoveries and insights. Documenting your findings serves several important purposes and can greatly enhance the effectiveness of your decision-making process.
Firstly, documenting your findings allows you to maintain a clear record of the information you have gathered. This ensures that you have accurate and reliable data readily available for reference as you move forward with your decision-making process. By organizing and documenting your findings, you create a valuable resource that can be easily accessed whenever needed.
Secondly, documenting your findings enables effective communication with stakeholders or team members involved in the decision-making process. Clear documentation allows you to share relevant information, insights, and conclusions with others, fostering better collaboration and understanding among team members. It helps avoid miscommunication or misunderstanding by providing a comprehensive overview of the evidence collected.
Furthermore, documenting your findings facilitates transparency and accountability. By keeping a detailed record of the data sources, analysis methods used, and results obtained, you establish a transparent decision-making process. This transparency builds trust among stakeholders as they can see how decisions are being made based on solid evidence rather than personal biases or arbitrary factors.
Moreover, documenting findings allows for future reference and learning from past experiences. Decision-making processes often involve recurring challenges or similar situations. By maintaining well-documented records of previous decisions made based on evidence, you can refer back to them when faced with similar circumstances in the future. This helps avoid reinventing the wheel and promotes continuous improvement in decision making.
In conclusion, documenting your findings is an essential tip in evidence-based decision making. It ensures that accurate information is readily available for reference and communication purposes, promotes transparency and accountability within the decision-making process, and facilitates learning from past experiences. By diligently recording your discoveries, you maximize the effectiveness of evidence-based decision making and increase the chances of making well-informed choices.