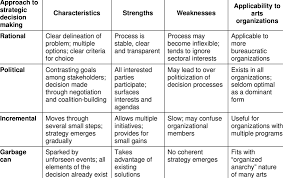
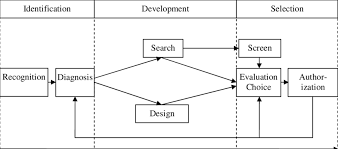
Programmed Decision Making Techniques: Streamlining Choices for Optimal Results
In today’s fast-paced and complex world, decision making has become an integral part of our daily lives. From personal choices to business strategies, the ability to make effective decisions is crucial for success. One approach that has gained significant attention is programmed decision making techniques.
Programmed decision making techniques refer to a set of predetermined rules or procedures that guide decision making in specific situations. These techniques are designed to simplify the decision-making process by providing a structured framework that can be applied repeatedly.
One commonly used programmed decision-making technique is the use of algorithms. An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure that outlines the necessary actions to reach a desired outcome. By following a predefined sequence of operations, individuals or organizations can make decisions quickly and efficiently.
Another technique employed in programmed decision making is the use of expert systems. Expert systems are computer-based programs that mimic human expertise in specific domains. These systems utilize vast amounts of knowledge and experience to provide recommendations or solutions based on predefined rules and logical reasoning.
Decision trees are yet another popular programmed decision-making technique. A decision tree visually represents various possible outcomes and their associated probabilities, helping individuals or organizations assess the potential consequences of different choices. By following a series of branches and nodes, one can determine the optimal course of action based on desired outcomes.
Furthermore, linear programming is widely used in business settings for optimizing resource allocation decisions. Linear programming involves formulating mathematical models that maximize or minimize an objective function while considering constraints such as limited resources or budgetary limitations.
The benefits of programmed decision making techniques are numerous. Firstly, these techniques save time by eliminating the need for extensive analysis and evaluation during every decision-making process. Instead, individuals can rely on established procedures or algorithms to arrive at conclusions swiftly.
Moreover, programmed decision making techniques enhance consistency and reduce bias in decision making. By following predetermined rules or relying on expert systems, subjective judgment can be minimized, leading to more objective and reliable outcomes.
Furthermore, programmed decision making techniques promote efficiency and productivity by streamlining decision-making processes. By utilizing algorithms, expert systems, or decision trees, individuals can make informed choices without getting overwhelmed by complex information or options.
However, it is important to note that programmed decision making techniques are not suitable for all situations. These techniques are most effective when applied to routine or recurring decisions that involve well-defined problems and known variables. In cases where creativity, intuition, or unique circumstances play a significant role, alternative decision-making approaches may be more appropriate.
In conclusion, programmed decision making techniques offer a valuable framework for simplifying and expediting the decision-making process. By utilizing algorithms, expert systems, decision trees, or linear programming methods, individuals and organizations can make informed choices efficiently and consistently. While these techniques have their limitations, when applied appropriately, they can greatly enhance the quality of decisions made in various domains.
8 Advantages of Programmed Decision Making Techniques
- Improved accuracy
- Increased speed
- Reduced costs
- Standardization
- Data-driven insights
- Improved compliance
- Increased transparency
- Reduced bias
Drawbacks of Programmed Decision Making Techniques: Examining the Lack of Human Judgment, Unforeseen Consequences, Costly Implementation, Limited Flexibility, and Bias
Improved accuracy
Improved Accuracy: Programmed Decision Making Techniques Enhance Precision in Decision-Making Processes
In the realm of decision making, accuracy is of paramount importance. A single erroneous choice can have far-reaching consequences, both personally and professionally. This is where programmed decision-making techniques come into play, offering a significant advantage by reducing errors and improving accuracy in decision-making processes.
Programmed decision-making techniques provide a structured framework that follows predefined rules or algorithms. By relying on these established procedures, individuals can minimize the likelihood of human error and ensure more precise outcomes.
One key way in which programmed decision-making techniques enhance accuracy is by eliminating subjective biases. Human judgment can be influenced by various factors such as emotions, personal beliefs, or cognitive limitations. These biases can cloud rational thinking and lead to flawed decisions.
By utilizing programmed techniques, individuals can mitigate these biases and make choices based on objective criteria. Algorithms, expert systems, or decision trees operate on logical reasoning and predefined rules, leaving little room for subjective biases to influence the decision-making process. As a result, the accuracy of decisions is significantly improved.
Moreover, programmed decision-making techniques offer consistency in the application of rules or procedures. Human beings are prone to inconsistencies due to factors like fatigue or variations in interpretation. These inconsistencies can lead to discrepancies in decision outcomes when faced with similar situations.
Programmed techniques provide a standardized approach that ensures consistent application of rules across different scenarios. By following predefined algorithms or expert systems’ recommendations consistently, individuals can achieve greater accuracy and reduce variations in their decision making.
Furthermore, programmed decision-making techniques enable individuals to consider a wide range of factors simultaneously without overlooking crucial details. These techniques facilitate comprehensive analysis by incorporating multiple variables into the decision-making process.
For instance, linear programming models allow businesses to optimize resource allocation decisions by considering numerous constraints simultaneously. This comprehensive approach minimizes oversights and enhances accuracy by accounting for all relevant factors involved in the decision.
In summary, programmed decision-making techniques offer a powerful tool for improving accuracy in decision making. By reducing subjective biases, ensuring consistency, and facilitating comprehensive analysis, these techniques enhance the precision of decisions made in various contexts. Whether it’s a routine choice or a complex business decision, programmed techniques provide a reliable framework to minimize errors and achieve more accurate outcomes.
Increased speed
Increased Speed: Accelerating Decision Making with Programmed Techniques
In today’s fast-paced world, time is of the essence, and organizations strive to make decisions swiftly and efficiently. One significant advantage of programmed decision making techniques is the increased speed they offer in processing data and reaching conclusions. By leveraging automated algorithms, organizations can expedite their decision-making processes, gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Automated decision-making algorithms are designed to analyze vast amounts of data rapidly. Unlike humans who may require extensive time for research, analysis, and evaluation, algorithms can process information at lightning speed. This allows organizations to quickly gather insights from various sources and make informed decisions promptly.
The speed at which programmed decision making techniques operate provides several benefits. Firstly, it enables organizations to respond swiftly to changing market conditions or emerging opportunities. In dynamic industries where time is critical, being able to make timely decisions can be a game-changer. Organizations that can adapt rapidly to market shifts have a higher chance of success.
Moreover, the increased speed of programmed decision making techniques allows for improved operational efficiency. By automating repetitive or routine decisions, organizations can eliminate bottlenecks caused by manual processes or delays in human decision making. This efficiency gain translates into cost savings and optimized resource allocation.
Additionally, faster decision making leads to enhanced customer satisfaction. Customers expect quick responses and resolutions from businesses they interact with. By leveraging programmed decision making techniques, organizations can provide rapid solutions or personalized recommendations based on customer preferences or historical data. This not only improves customer experience but also strengthens brand loyalty.
However, while increased speed is undoubtedly a pro of programmed decision making techniques, it is crucial to strike a balance between speed and accuracy. Rapid decisions are beneficial only if they are based on reliable data and sound logic. Organizations must ensure that their algorithms are well-designed and regularly updated to avoid potential biases or errors that could compromise the quality of decisions made.
In conclusion, the increased speed offered by programmed decision making techniques is a significant advantage for organizations. By leveraging automated algorithms, businesses can process vast amounts of data quickly, enabling them to make informed decisions in a timely manner. This speed enhances their ability to adapt to market changes, improves operational efficiency, and enhances customer satisfaction. However, organizations must remain vigilant in maintaining the accuracy and reliability of their programmed decision-making systems to ensure optimal outcomes.
Reduced costs
Reduced Costs: The Cost-Saving Advantage of Programmed Decision Making Techniques
In today’s fast-paced world, time is money. Every moment wasted in decision-making processes can have a significant impact on an organization’s bottom line. This is where programmed decision making techniques come to the rescue, offering a valuable solution for reducing costs.
One prominent benefit of programmed decision making techniques is their ability to automate decisions. By utilizing algorithms, expert systems, or other predefined rules, organizations can streamline their decision-making processes and eliminate the need for extensive manual labor. This automation not only saves time but also reduces the associated costs.
When decisions are automated, the need for human involvement in repetitive or routine tasks decreases significantly. This means that employees can focus their efforts on more complex and strategic activities that require their expertise and creativity. By freeing up human resources from mundane decision-making tasks, organizations can optimize their workforce and allocate it more effectively across various areas.
Furthermore, programmed decision making techniques eliminate delays commonly associated with human input. Humans are prone to errors and inconsistencies due to factors such as fatigue, emotions, or biases. These factors can lead to longer processing times and potentially costly mistakes. By automating decisions through programmed techniques, organizations can minimize these delays and ensure consistent and accurate outcomes.
Additionally, reducing manual labor in decision-making processes reduces the overall operational costs of an organization. Hiring individuals solely for repetitive decision-making tasks can be expensive in terms of recruitment, training, salaries, benefits, and other associated expenses. By leveraging programmed techniques instead, organizations can achieve cost savings by minimizing the need for additional personnel dedicated solely to decision making.
Moreover, automated decisions provide a faster turnaround time compared to traditional manual approaches. This speed is particularly beneficial in time-sensitive situations where quick decisions are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge or seizing opportunities. By swiftly processing large amounts of data and providing instant recommendations or solutions through programmed techniques, organizations can seize opportunities promptly while avoiding potential financial losses.
In conclusion, programmed decision making techniques offer a significant advantage in terms of cost reduction. By automating decisions, organizations can save time and money by eliminating the need for manual labor and minimizing delays associated with human input. This cost-saving benefit allows organizations to allocate resources more efficiently, optimize their workforce, and make timely decisions that positively impact their bottom line. Embracing programmed decision making techniques can pave the way for increased efficiency, productivity, and financial success.
Standardization
Standardization: Enhancing Consistency and Alignment with Programmed Decision Making Techniques
In today’s dynamic business environment, consistency and alignment are key factors for success. This is where programmed decision making techniques shine, offering a pro that can greatly benefit organizations: standardization.
Programmed decision making techniques provide a structured framework that allows for a consistent approach to decision making. By following predefined rules, algorithms, or expert systems, organizations can ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page when it comes to how decisions are made.
Standardization brings several advantages to the table. Firstly, it promotes clarity and transparency within an organization. When decision-making processes are standardized, everyone involved understands the steps and criteria used to reach conclusions. This shared understanding helps eliminate confusion and promotes effective communication among team members.
Moreover, standardization fosters fairness and equality. By utilizing programmed decision making techniques, organizations can ensure that decisions are made based on objective criteria rather than personal biases or preferences. This reduces the potential for favoritism or discrimination and creates a level playing field for all stakeholders involved.
Consistency in decision making also leads to enhanced efficiency. When individuals across an organization follow the same procedures or guidelines provided by programmed decision making techniques, time is saved by avoiding unnecessary debates or delays caused by inconsistent approaches. This increased efficiency allows organizations to focus their resources on other critical tasks and initiatives.
Additionally, standardization helps organizations maintain quality control. By using programmed decision making techniques, organizations can establish benchmarks or standards for evaluating options and outcomes consistently. This enables them to monitor performance, identify areas for improvement, and implement necessary adjustments to enhance overall effectiveness.
Furthermore, standardization through programmed decision making techniques facilitates organizational learning and knowledge sharing. When decisions are made using predefined rules or expert systems, organizations can capture valuable insights from successful outcomes or learn from past mistakes. This accumulated knowledge can then be shared across teams or departments, fostering continuous improvement in decision-making processes.
However, it is important to note that standardization should not stifle creativity or innovation. While programmed decision making techniques provide a consistent framework, organizations should also encourage flexibility and adaptability when faced with unique or complex situations. It is crucial to strike a balance between standardization and the need for agile decision making in rapidly changing environments.
In conclusion, standardization is a significant advantage of programmed decision making techniques. By providing a consistent approach to decision making, organizations can enhance clarity, fairness, efficiency, quality control, and knowledge sharing. Embracing standardized processes can help align stakeholders and ensure that decisions are made in a transparent and objective manner.
Data-driven insights
Data-driven insights: Unlocking the Power of Programmed Decision Making Techniques
In today’s data-driven world, organizations are constantly seeking ways to extract valuable insights from the vast amounts of information available to them. One significant advantage of programmed decision making techniques is their ability to leverage data and provide valuable insights that may otherwise go unnoticed.
Automated decision making algorithms have the capability to analyze large volumes of data in real-time, identifying patterns, trends, and correlations that humans may overlook. By processing this data efficiently, organizations can gain a competitive edge by making better-informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information.
These programmed decision making techniques allow organizations to tap into a wealth of data sources, including customer behavior, market trends, social media sentiment, and more. By analyzing these diverse datasets simultaneously, algorithms can uncover hidden insights that humans may struggle to identify manually.
The ability to access real-time information is particularly advantageous in dynamic industries where market conditions change rapidly. With programmed decision making techniques, organizations can stay ahead of the curve by quickly adapting their strategies based on emerging trends or shifts in consumer preferences.
Moreover, these techniques enable organizations to make decisions based on objective data rather than relying solely on intuition or subjective judgment. By eliminating human bias and emotion from the decision-making process, organizations can make more rational choices that are grounded in empirical evidence.
Programmed decision making techniques also facilitate predictive analytics. By analyzing historical data and identifying recurring patterns or correlations, algorithms can forecast future outcomes with a reasonable degree of accuracy. This enables organizations to anticipate potential challenges or opportunities and proactively adjust their strategies accordingly.
Furthermore, these techniques offer scalability and efficiency by automating the analysis process. Instead of manually sifting through massive amounts of data, algorithms can handle this task swiftly and accurately. This frees up valuable time for employees to focus on higher-level tasks such as strategy development or creative problem-solving.
However, it is important for organizations to exercise caution when relying solely on programmed decision making techniques. While algorithms can provide valuable insights, they should not be seen as a replacement for human judgment and expertise. Human oversight is still crucial to interpret the results, validate the findings, and consider contextual factors that may not be captured by the data alone.
In conclusion, programmed decision making techniques offer organizations a powerful tool to unlock data-driven insights. By leveraging automated algorithms, organizations can gain valuable real-time information, identify trends and patterns, and make better-informed decisions. However, it is essential to remember that these techniques should be used in conjunction with human expertise to ensure a holistic approach to decision making. When utilized effectively, programmed decision making techniques can provide organizations with a competitive edge in today’s data-driven landscape.
Improved compliance
Improved Compliance: Streamlining Decision Making for Regulatory Adherence
In today’s ever-evolving regulatory landscape, organizations face the challenge of staying compliant with numerous laws and regulations. This is where programmed decision making techniques come to the rescue, offering a significant advantage in terms of improved compliance.
By automating certain decisions through programmed decision making techniques, organizations can ensure that their processes align with relevant laws and regulations. This eliminates the need for manual checks at every step of the process whenever a new regulation is introduced or amended.
One key benefit of programmed decision making techniques in terms of compliance is the ability to incorporate legal requirements directly into the decision-making algorithms or expert systems. This means that as regulations change, organizations can update their automated processes accordingly, ensuring ongoing adherence without extensive manual intervention.
This approach not only saves valuable time and resources but also minimizes the risk of human error in compliance-related decisions. By relying on predefined rules and logical reasoning within programmed systems, organizations can reduce subjectivity and bias, thus enhancing consistency and accuracy in meeting regulatory requirements.
Moreover, programmed decision making techniques enable organizations to proactively address compliance concerns. Instead of reacting to regulatory changes after they occur, organizations can anticipate potential updates and incorporate them into their automated decision-making processes ahead of time. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks associated with non-compliance and ensures that operations continue smoothly while meeting legal obligations.
Additionally, by automating compliance-related decisions, organizations can enhance transparency and auditability. The use of programmed techniques provides a clear trail of decisions made based on specific rules or algorithms. This auditable record not only facilitates internal monitoring but also aids external audits or inspections by regulatory authorities.
It is important to note that while programmed decision making techniques offer improved compliance benefits, they should be used in conjunction with human oversight. Human judgment remains essential in assessing complex situations or interpreting ambiguous regulations where automation may fall short. Therefore, a balanced approach that combines automated decision making with human expertise is crucial for optimal compliance outcomes.
In conclusion, programmed decision making techniques play a vital role in improving compliance for organizations. By automating certain decisions and incorporating legal requirements into algorithms or expert systems, organizations can ensure ongoing adherence to regulations. This approach saves time, reduces human error, enables proactive compliance measures, and enhances transparency. However, it is essential to strike a balance between automation and human oversight to address complex scenarios effectively. With programmed decision making techniques as a powerful tool, organizations can navigate the regulatory landscape with greater ease and confidence.
Increased transparency
Increased Transparency: Building Trust and Accountability through Programmed Decision Making Techniques
In today’s complex business landscape, transparency has become a crucial aspect of organizational success. One significant advantage of programmed decision making techniques is the increased transparency they bring to the decision-making process. By utilizing automated systems, stakeholders within and outside an organization gain a clearer understanding of why specific decisions were made and how they impact various aspects of the business.
Automated decision making systems provide a structured framework that follows predefined rules or algorithms. This means that the rationale behind each decision is based on established guidelines, making it easier for stakeholders to comprehend the logic behind the chosen course of action. Whether it’s employees, customers, clients, or partners, having access to this information fosters trust and confidence in an organization’s decision-making processes.
Transparency in decision making also extends beyond understanding why a particular choice was made. It encompasses comprehending how that decision influences other areas of the business or its stakeholders. Programmed decision making techniques enable organizations to map out potential impacts and consequences more accurately.
For example, when using automated systems like expert systems or decision trees, stakeholders can visualize different outcomes and understand how each choice affects various departments, customers, clients, or partners. This level of visibility helps stakeholders make informed judgments about the decisions being made and allows them to assess potential risks or benefits more effectively.
By providing increased transparency through programmed decision making techniques, organizations can enhance accountability within their operations. Stakeholders can hold decision makers responsible for their choices since they have access to the underlying rationale and impact analysis. This accountability improves overall operational efficiency as it encourages individuals involved in decision making to act responsibly and consider all relevant factors before finalizing any choices.
Moreover, increased transparency also promotes a culture of open communication within an organization. When stakeholders have clear insights into why decisions are made and how they affect different areas of the business, it becomes easier for them to engage in meaningful discussions or provide valuable feedback. This collaborative environment fosters innovation, as stakeholders can contribute their expertise and perspectives to refine decision-making processes further.
In conclusion, programmed decision making techniques offer the advantage of increased transparency in the decision-making process. By utilizing automated systems and predefined rules, stakeholders gain a clearer understanding of why decisions were made and how they impact various aspects of the business or its stakeholders. This transparency builds trust, fosters accountability, and promotes open communication within an organization. Embracing programmed decision making techniques can lead to more informed choices and ultimately contribute to the overall success of an organization.
Reduced bias
Reduced Bias: The Power of Programmed Decision Making Techniques
In today’s diverse and dynamic world, bias can often seep into decision-making processes, leading to suboptimal outcomes. However, one significant advantage of programmed decision making techniques is their ability to reduce bias and promote more objective decision making.
By automating certain aspects of the decision-making process, organizations can minimize the potential influence of personal biases. Unlike humans who may have different opinions or preferences when it comes to certain topics or issues, automated systems are designed to follow predefined rules and logical reasoning.
Automated decision-making systems operate based on objective criteria and data-driven algorithms. They are not swayed by emotions, personal beliefs, or subjective judgments that can introduce bias into the decision-making process. This reduction in bias ensures that decisions are made consistently and impartially.
Moreover, programmed decision making techniques provide a level playing field for everyone involved. Human biases such as stereotypes or prejudices can inadvertently impact decisions and perpetuate inequalities. By relying on automated systems, organizations can help mitigate these biases and create a fairer environment for all individuals affected by the decisions.
Programmed decision making techniques also offer transparency in the decision-making process. With clear rules and predefined criteria guiding the decisions, it becomes easier to identify any potential biases that might exist within the system itself. This transparency allows for continuous improvement and refinement of the automated systems to ensure fairness and accuracy.
Reducing bias through programmed decision making techniques not only leads to fairer outcomes but also enhances trust in the decision-making process. When individuals perceive that decisions are being made objectively without favoritism or discrimination, they are more likely to accept those decisions even if they may not align with their personal preferences.
However, it is important to acknowledge that programmed decision making techniques are not entirely immune to bias themselves. Biases can still be present if they are inadvertently built into algorithms or if data used for training these systems contains inherent biases. Therefore, constant monitoring and evaluation are necessary to identify and rectify any potential biases that may arise.
In conclusion, programmed decision making techniques have the power to reduce bias and promote more objective decision making. By automating certain aspects of decision making, organizations can minimize the influence of personal biases and ensure a fairer, more transparent process. Leveraging these techniques not only improves the quality of decisions but also fosters trust and confidence in the decision-making process as a whole.
Lack of Human Judgment
Lack of Human Judgment: A Consideration in Programmed Decision Making Techniques
While programmed decision making techniques offer numerous advantages, it is important to acknowledge one potential con: the lack of human judgment. In decision making processes guided solely by algorithms, expert systems, or predefined rules, there is a risk of overlooking the nuance and complexity that human judgment brings.
Human judgment encompasses a range of factors such as intuition, emotions, and contextual understanding that may not be fully captured by programmed decision making techniques. These techniques often rely on logical reasoning and predefined rules to arrive at conclusions. As a result, decisions made through these methods can sometimes be overly simplistic or fail to consider the unique aspects of an individual situation.
One key aspect of human judgment is the ability to adapt and respond to unforeseen circumstances. Programmed decision making techniques are typically designed for specific scenarios and may not account for unexpected variables or changing conditions. In such cases, relying solely on programmed techniques can limit the flexibility needed to make appropriate adjustments.
Additionally, human judgment takes into account subjective factors that may not be easily quantifiable or captured within rigid decision-making frameworks. Intuition and gut feelings play a role in decision making that cannot be replicated by algorithms alone. These subjective elements often contribute to more holistic and personalized decisions that align with individual values, preferences, or organizational culture.
Another consideration is ethical decision making. Programmed techniques may struggle when confronted with ethical dilemmas that require moral reasoning and consideration of various stakeholders’ interests. Ethical decisions often involve weighing conflicting values and evaluating long-term consequences—a task that requires complex human judgment beyond what programmed systems can provide.
However, it’s important to note that programmed decision making techniques can still be valuable tools when used in conjunction with human judgment. By combining the strengths of both approaches—utilizing structured frameworks while incorporating critical thinking and contextual understanding—more robust decisions can be made.
In conclusion, while programmed decision making techniques offer efficiency and consistency, they should be used with caution. The lack of human judgment can limit the ability to account for nuanced factors, adapt to unforeseen circumstances, or address ethical complexities. By recognizing this limitation and integrating human judgment into the decision-making process, we can strike a balance that leverages the benefits of both approaches, leading to more well-rounded and effective decisions.
Unforeseen Consequences
Unforeseen Consequences: The Limitations of Programmed Decision Making Techniques
Programmed decision making techniques have undoubtedly revolutionized the way we approach decision making, providing structure and efficiency to the process. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that these techniques are not without their limitations. One significant drawback is the potential for unforeseen consequences arising from their limited scope and inability to accurately anticipate all possible outcomes.
Programmed decision making techniques rely on predefined rules, algorithms, or expert systems to guide choices. While these frameworks are designed to streamline decision making and promote consistency, they may overlook certain nuances or variables that can lead to unintended consequences.
One challenge lies in the complexity of real-world scenarios. Many decisions involve intricate interdependencies and dynamic environments that may not fit neatly into predetermined rules or algorithms. As a result, programmed decision making techniques may fail to account for all relevant factors, leading to incomplete analyses and potentially unfavorable outcomes.
Moreover, programmed decision making techniques often assume a level of predictability that may not align with reality. In complex systems where multiple factors interact, it is difficult to accurately forecast all potential outcomes. Unforeseen circumstances or external influences can disrupt the expected chain of events, rendering programmed decisions inadequate or even detrimental.
Another limitation arises from the lack of creativity and adaptability in programmed decision making techniques. These methods typically rely on historical data or established rules, which may hinder innovative thinking or flexible responses to unique situations. The rigidity of these approaches can limit exploration of alternative options or consideration of novel solutions that could potentially yield better results.
Furthermore, programmed decision making techniques may overlook ethical considerations or human values that cannot be easily quantified or captured by algorithms. Certain decisions require a deeper understanding of moral implications, social impact, or individual perspectives – aspects that programmed techniques might struggle to incorporate effectively.
To mitigate these limitations, it is crucial for individuals and organizations utilizing programmed decision making techniques to remain vigilant and supplement them with critical thinking and human judgment. Recognizing the potential for unforeseen consequences, decision makers should actively consider the limitations of programmed techniques and be prepared to adapt or modify their approach as necessary.
In conclusion, while programmed decision making techniques offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency and consistency, they are not infallible. Unforeseen consequences can arise due to their limited scope and inability to anticipate all possible outcomes accurately. It is essential to recognize these limitations, exercise caution, and supplement programmed techniques with human judgment to ensure decisions are well-informed and aligned with desired goals.
Costly Implementation
Costly Implementation: A Consideration in Programmed Decision Making Techniques
While programmed decision making techniques offer numerous benefits, it is important to acknowledge that their implementation can come with a potential drawback: cost. Adopting and integrating these techniques into an organization’s decision-making processes often requires a substantial investment of resources.
One significant cost associated with implementing programmed decision making techniques is the development or acquisition of the necessary tools and technologies. Creating algorithms, expert systems, or decision tree models can be a complex and time-consuming task that may require the expertise of skilled professionals or the purchase of specialized software.
Furthermore, maintaining and updating these tools is an ongoing expense. As new information becomes available or business conditions change, programmed decision making techniques must be regularly reviewed and refined to ensure their accuracy and relevance. This necessitates allocating resources for continuous monitoring, maintenance, and improvement.
Another cost consideration lies in training personnel to effectively utilize these techniques. Employees need to understand how to navigate the software or systems involved, interpret the generated recommendations or outcomes correctly, and make informed decisions based on the outputs provided. Providing comprehensive training programs can require both time and financial investments.
Additionally, organizations may need to allocate resources for technical support or consulting services to address any issues that arise during implementation or usage. This can include troubleshooting software glitches, resolving compatibility problems with existing systems, or seeking guidance on optimizing the effectiveness of programmed decision making techniques.
It is crucial for organizations to carefully evaluate the potential return on investment when considering programmed decision making techniques. While these techniques can enhance efficiency and improve decision-making outcomes in certain contexts, it is essential to weigh their benefits against the costs associated with their implementation.
In conclusion, while programmed decision making techniques offer valuable advantages in terms of streamlining decisions and reducing bias, it is important to recognize that their implementation can be costly. Organizations must assess whether the benefits outweigh the expenses involved in developing, maintaining, and training personnel on these techniques before deciding if they are the right fit for their specific needs and resources.
Limited Flexibility
Limited Flexibility: A Drawback of Programmed Decision Making Techniques
Programmed decision making techniques have undoubtedly revolutionized the way we approach decision making, providing structure and efficiency. However, like any approach, they are not without their limitations. One significant drawback of programmed decision making techniques is their limited flexibility.
These techniques are designed with a specific purpose in mind, with predefined rules and procedures that guide the decision-making process. While this can be advantageous in routine or recurring situations, it becomes a challenge when faced with new or unpredictable circumstances.
In a rapidly changing world, where conditions and variables can shift unexpectedly, programmed decision making techniques may struggle to adapt quickly. The rigid nature of these techniques can hinder the ability to respond effectively to emerging challenges or seize new opportunities.
The predetermined rules and algorithms that govern programmed decision making may not account for all possible scenarios or account for unique circumstances. This lack of flexibility can lead to suboptimal decisions or missed opportunities if the predefined framework does not align with the current situation.
Moreover, as new information becomes available or conditions change, programmed decision making techniques may not be able to incorporate these factors adequately. This limitation can result in outdated or irrelevant decisions that do not reflect the current reality.
Furthermore, programmed decision making techniques rely heavily on historical data and past experiences to guide decision-making processes. While this can provide a solid foundation for many situations, it may overlook innovative approaches or creative solutions that deviate from established norms.
To overcome this limitation, it is crucial to strike a balance between using programmed decision making techniques and allowing room for flexibility and adaptability. Recognizing the inherent limitations of these techniques is essential in order to supplement them with other approaches when faced with novel or complex situations.
In conclusion, while programmed decision making techniques offer structure and efficiency in decision making, their limited flexibility can be a significant drawback. It is important to acknowledge that these techniques may not always be suitable for every situation and that alternative approaches may be necessary to address new or changing conditions effectively. By understanding the limitations and exploring complementary methods, we can enhance our decision-making processes and navigate the ever-evolving landscape with greater agility.
Bias
Bias: A Challenge in Programmed Decision Making Techniques
Programmed decision making techniques have undoubtedly revolutionized the way we approach decision making, offering efficiency and consistency. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that these techniques are not without their flaws. One significant concern that arises with programmed decision making techniques is the potential for bias.
Algorithms, which form the backbone of many programmed decision making techniques, rely on data for their training and operation. If the data used to train these algorithms contain biases, whether intentional or unintentional, it can lead to unfair outcomes for certain individuals or groups of people.
One source of bias in programmed decision making techniques is the data itself. If historical data used to train an algorithm reflects existing societal biases or discrimination, those biases can be perpetuated in the decision-making process. For example, if a hiring algorithm is trained on historical employment data that favors certain demographics over others, it may inadvertently perpetuate discriminatory hiring practices.
Additionally, assumptions made by algorithms about how people should behave in certain situations can introduce bias as well. These assumptions are often based on existing social norms and values, which may not be universally applicable or fair. If an algorithm assumes that individuals from a particular background should exhibit specific behaviors or preferences, it can lead to biased outcomes for those who deviate from those assumptions.
Furthermore, there is also a risk of bias when it comes to defining what constitutes a “good” outcome within programmed decision making techniques. The criteria used to evaluate outcomes may inadvertently favor certain groups or perspectives while marginalizing others. This can result in unequal treatment or disadvantage for individuals who do not align with the predefined criteria.
Addressing bias in programmed decision making techniques requires continuous effort and vigilance. It involves critically examining the training data used for algorithms and ensuring its representativeness and fairness. Additionally, transparency and accountability in algorithmic decision-making processes are essential so that potential biases can be identified and rectified.
Moreover, involving diverse perspectives and expertise in the development and evaluation of programmed decision making techniques can help mitigate bias. By incorporating a range of voices and experiences, it is possible to challenge assumptions, identify potential biases, and create more inclusive decision-making processes.
In conclusion, while programmed decision making techniques offer significant benefits, it is important to recognize and address the issue of bias. Bias can arise from the data used to train algorithms or the assumptions made within these techniques. By actively working towards fairness, transparency, and inclusivity in the design and implementation of programmed decision making techniques, we can strive for more equitable outcomes that benefit all individuals and groups in our society.