Strategic Decisions in Operations: Enhancing Efficiency and Success
In the dynamic and competitive business landscape, strategic decision-making plays a pivotal role in the success of any organization. When it comes to operations, making well-informed and forward-thinking strategic decisions is essential for enhancing efficiency, optimizing resources, and gaining a competitive edge.
Operations encompass the core activities that drive an organization’s day-to-day functioning, including production, supply chain management, distribution, and service delivery. Strategic decisions in operations involve long-term planning and goal-setting to ensure that these activities align with the overall organizational strategy.
One crucial aspect of strategic decision-making in operations is optimizing processes. This involves analyzing the existing workflows, identifying bottlenecks or inefficiencies, and implementing improvements to streamline operations. By identifying areas of improvement and implementing process enhancements or automation technologies, organizations can increase productivity while reducing costs.
Another key consideration in strategic decision-making is capacity planning. Organizations need to assess their current capabilities and forecast future demand to make informed decisions about resource allocation. This includes determining the appropriate level of staffing, machinery, inventory levels, and infrastructure required to meet customer demands efficiently. Strategic capacity planning ensures that organizations can scale their operations effectively without compromising quality or incurring unnecessary expenses.
Supply chain management is another critical area where strategic decisions can have a significant impact. Organizations must evaluate their supplier relationships, logistics networks, inventory management systems, and distribution channels to optimize efficiency while minimizing costs. By strategically selecting suppliers based on factors such as reliability, cost-effectiveness, and quality standards, organizations can ensure a smooth flow of materials and minimize disruptions.
Strategic decisions in operations also involve risk management considerations. Organizations must proactively identify potential risks such as supply chain disruptions, natural disasters, or regulatory changes that could impact their operations. By developing contingency plans and implementing risk mitigation strategies ahead of time, organizations can minimize the negative impact on their operations when unforeseen events occur.
Furthermore, technology adoption is an integral part of strategic decision-making in operations. Embracing digital transformation and leveraging emerging technologies can revolutionize operations, improve efficiency, and enhance customer experiences. Technologies such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, Internet of Things (IoT), and automation can optimize processes, enable real-time decision-making, and drive innovation.
Lastly, strategic decisions in operations require a holistic approach that considers the broader organizational goals. Operations should align with the overall business strategy to ensure consistency and cohesiveness. This includes considering factors such as market trends, customer preferences, competitive landscape, and financial objectives when making operational decisions.
In conclusion, strategic decision-making in operations is crucial for organizations aiming to achieve efficiency and success. By optimizing processes, planning capacity effectively, managing supply chains strategically, mitigating risks proactively, embracing technology advancements, and aligning with overall organizational goals, businesses can enhance their operational performance and gain a competitive advantage in today’s dynamic marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions: Strategic Decisions in Operations
- What are the 5 key characteristics of a strategic decision?
- What are the 10 strategic decisions in operations management?
- What are examples of strategic decisions?
- What are the four types of strategic decisions?
What are the 5 key characteristics of a strategic decision?
The five key characteristics of a strategic decision are as follows:
- Long-term Impact: Strategic decisions have a significant and lasting impact on the organization. They are not short-term fixes but rather choices that shape the direction and future of the organization. These decisions often involve substantial resources, time, and effort.
- Cross-Functional: Strategic decisions cut across various departments and functions within an organization. They require input and collaboration from different stakeholders, including senior executives, department heads, and subject matter experts. These decisions consider the broader implications on different areas of the organization to ensure alignment and coherence.
- Future-Oriented: Strategic decisions focus on future opportunities, challenges, and goals rather than solely addressing current issues. They involve forecasting trends, analyzing market dynamics, understanding customer needs, and anticipating potential changes in the business environment. By taking a forward-looking approach, organizations can proactively position themselves for success.
- Uncertainty and Complexity: Strategic decisions often involve dealing with ambiguity, uncertainty, and complexity. The business landscape is constantly evolving with numerous external factors that can impact decision-making. Leaders must carefully analyze available information while acknowledging that some aspects may be uncertain or subject to change.
- Commitment of Resources: Strategic decisions require a commitment of resources such as financial investments, human capital, technology infrastructure, or research and development efforts. These decisions allocate resources strategically to support organizational goals while balancing risks and rewards.
By possessing these key characteristics—long-term impact, cross-functional collaboration, future orientation, handling uncertainty/complexity effectively, and committing resources strategically—an organization can make informed strategic decisions that drive success in today’s dynamic business environment.
What are the 10 strategic decisions in operations management?
In operations management, there are various strategic decisions that organizations make to enhance efficiency and achieve their objectives. While the specific strategic decisions may vary depending on the industry and organization, here are 10 common strategic decisions in operations management:
- Product and Service Design: Decisions related to the design of products or services, including features, specifications, quality standards, and customization options.
- Process Selection: Choosing the most appropriate production or service delivery process, such as job shop, assembly line, or continuous flow, based on factors like volume, variety, and customer requirements.
- Capacity Planning: Determining the optimal level of resources (e.g., labor, machinery) required to meet current and future demand while balancing costs and customer satisfaction.
- Facility Location: Identifying suitable locations for facilities like manufacturing plants or distribution centers based on factors such as proximity to suppliers/customers, transportation infrastructure, labor availability, and cost considerations.
- Layout Design: Deciding on the arrangement of equipment, workstations, storage areas within a facility to optimize workflow efficiency and minimize waste (e.g., through cellular layout or product-focused layout).
- Supply Chain Management: Making decisions regarding supplier selection and management, inventory management strategies (e.g., Just-in-Time), transportation modes/routes optimization, and collaboration with partners for efficient material flow.
- Quality Management: Establishing quality standards (e.g., Six Sigma), implementing quality control measures (e.g., statistical process control), and ensuring continuous improvement through methodologies like Lean Six Sigma.
- Inventory Management: Determining optimal inventory levels (e.g., Economic Order Quantity) to balance costs associated with holding inventory against potential stockouts or production delays.
- Maintenance Strategy: Developing maintenance plans to ensure optimal performance of equipment/machinery through preventive maintenance schedules or predictive maintenance techniques using data analytics.
- Human Resource Management: Making decisions related to workforce planning (e.g., hiring strategies), training and development programs, performance management systems, and employee engagement initiatives to enhance productivity and job satisfaction.
These strategic decisions in operations management are interconnected and require careful consideration to align with overall organizational goals and market dynamics. By making informed decisions in these areas, organizations can optimize their operations, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver value to customers.
What are examples of strategic decisions?
Strategic decisions are high-level decisions that have a significant impact on an organization’s long-term goals and direction. Here are some examples of strategic decisions across different areas of business:
- Market Expansion: Deciding to enter new markets or expand into new geographic regions to reach a larger customer base and increase market share.
- Product Development: Choosing to invest in research and development to create new products or improve existing ones, ensuring the organization stays competitive and meets evolving customer needs.
- Merger or Acquisition: Deciding to merge with or acquire another company as a strategic move to gain access to new markets, technologies, or resources.
- Pricing Strategy: Determining the pricing structure for products or services based on factors such as market demand, competition, and profitability goals.
- Outsourcing: Opting to outsource certain functions or processes to external vendors or partners in order to reduce costs, improve efficiency, or access specialized expertise.
- Strategic Partnerships: Forming alliances with other organizations to leverage their expertise, resources, or distribution channels for mutual benefit and growth.
- Technology Adoption: Making decisions about adopting new technologies or upgrading existing systems to streamline operations, enhance productivity, or improve customer experiences.
- Talent Management: Developing strategies for attracting, retaining, and developing a skilled workforce that aligns with the organization’s long-term goals and culture.
- Branding and Marketing Strategy: Deciding on the positioning, messaging, and channels for promoting the organization’s brand and products/services in order to build awareness and drive customer engagement.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Making strategic decisions related to environmental sustainability practices such as reducing carbon footprint, implementing renewable energy sources, or adopting sustainable supply chain practices.
These examples illustrate how strategic decisions cut across various aspects of business operations and require careful analysis of internal capabilities, market dynamics, competition, and long-term goals in order to drive success and achieve desired outcomes.
What are the four types of strategic decisions?
The four types of strategic decisions are as follows:
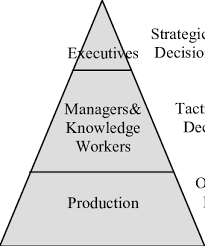
- Corporate-Level Decisions: These decisions focus on the overall direction and scope of the organization. They involve determining the industries or markets in which the organization should operate, evaluating potential mergers or acquisitions, and deciding on diversification strategies. Corporate-level decisions shape the organization’s portfolio of businesses and set the foundation for its long-term growth and profitability.
- Business-Level Decisions: These decisions are concerned with how a business unit or division within an organization competes in a specific market or industry. Business-level decisions involve formulating competitive strategies to gain a sustainable advantage over rivals, identifying target customer segments, and positioning products or services in the marketplace. These decisions aim to create value for customers while generating profits for the organization.
- Functional-Level Decisions: These decisions pertain to specific functional areas within an organization, such as marketing, operations, finance, human resources, and research and development. Functional-level decisions focus on optimizing resources and capabilities within each department to support the overall business strategy. For example, marketing decisions may involve pricing strategies, promotional campaigns, or market research initiatives.
- Operational-Level Decisions: These decisions are tactical in nature and deal with day-to-day activities necessary for executing organizational plans effectively. Operational-level decisions focus on managing resources efficiently, ensuring smooth production processes, optimizing supply chain operations, and delivering high-quality products or services to customers. Examples of operational-level decisions include inventory management strategies, production scheduling, workforce allocation, and quality control measures.
These four types of strategic decisions occur at different levels within an organization but are interconnected and influence one another. Effective coordination among these decision levels is essential for aligning organizational goals and achieving success in today’s competitive business environment.