Strategic Decision and Operational Decision: Understanding the Difference
In the world of business and management, decision-making plays a crucial role in determining the success or failure of an organization. Two types of decisions that are often encountered are strategic decisions and operational decisions. While both are important, it is essential to understand the differences between them and how they impact an organization’s overall objectives.
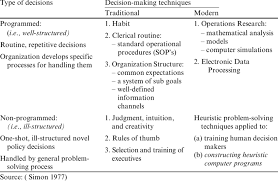
Strategic decisions are high-level decisions that shape the long-term direction and goals of an organization. These decisions involve allocating resources, setting priorities, and determining the overall strategy to achieve competitive advantage. Strategic decisions are typically made by top-level executives or senior management who have a broader perspective on the organization’s vision, mission, and external environment.
When making strategic decisions, managers consider factors such as market trends, competitor analysis, technological advancements, and customer demands. Examples of strategic decisions include entering new markets, launching new products or services, mergers and acquisitions, diversification strategies, and major investments in research and development.
On the other hand, operational decisions are day-to-day decisions that focus on executing the strategy set by strategic decision-makers. These decisions deal with routine activities aimed at achieving short-term objectives and ensuring smooth operations within an organization. Operational decisions are made by middle-level or lower-level managers who oversee specific departments or functions.
Operational decisions involve managing resources efficiently to meet production targets, optimizing supply chain processes, scheduling employee shifts, managing inventory levels, addressing customer complaints promptly, and ensuring quality control measures are in place. These decisions require a deep understanding of internal operations and often rely on data-driven analysis to improve efficiency.
While strategic decisions have a long-term impact on an organization’s direction and competitive position in the market, operational decisions focus on maintaining day-to-day operations smoothly to support strategic goals. Both types of decision-making are interconnected; effective operational decision-making supports successful implementation of strategic plans.
It is important for organizations to strike a balance between strategic decision-making and operational decision-making. Strategic decisions provide the overall vision and direction, while operational decisions ensure that the strategy is executed effectively. Without proper alignment between these two types of decision-making, organizations may struggle to achieve their desired outcomes.
In conclusion, strategic decisions and operational decisions are distinct but interconnected aspects of decision-making in organizations. Strategic decisions set the long-term direction and goals, while operational decisions focus on executing day-to-day activities to support those goals. Understanding the differences between these two types of decisions is crucial for managers at all levels to make informed choices that contribute to the overall success of an organization.
Strategic decisions provide organizational direction and align operational decisions with mission and goals.
Strategic decisions focus on long-term objectives, allowing for better planning and risk management.
3. Strategic decisions enable proactive responses
- Strategic decisions provide direction for the organization and help to ensure that all operational decisions are in line with the overall mission and goals.
- Strategic decisions focus on long-term objectives, allowing for more planning time and better risk management.
- Strategic decisions allow organizations to be proactive rather than reactive, helping them to anticipate changes in the environment or market conditions.
- Strategic decisions can result in greater efficiency since they tend to involve fewer resources and less complexity than operational decisions do.
- Operational decisions are made quickly, often with limited information available at the time of decision making, which helps organizations respond quickly to changing conditions or opportunities in their environment or market place.
- Operational decisions enable organizations to take advantage of short-term opportunities that may not fit into a strategic plan but could still benefit the organization’s overall goals and objectives over time.
- Operational decision making is usually less costly than strategic decision making due to its shorter timeline and more focused scope of analysis needed for each decision made within it’s shorter timeframe .
- Operational decision making allows managers more flexibility when responding quickly to new challenges or situations as they arise without having to wait for approval from higher levels of management within an organization .
- Operational decision making enables managers at lower levels of an organization have autonomy over certain aspects of their job responsibilities which can lead increased motivation among employees due its empowering nature
The Hidden Costs and Risks of Strategic and Operational Decision Making
- Strategic decisions can be costly and time consuming as they require a lot of research, analysis, and planning.
- Strategic decisions may not always provide immediate results or feedback on the effectiveness of the decision taken.
- Operational decisions are often made quickly and without adequate consideration of long-term implications or impacts on other areas of the business.
- Operational decisions can lead to an increase in operational costs if not properly managed or monitored over time.
- Strategic decisions can be difficult to reverse once implemented due to their complexity and far reaching implications for the business as a whole.
- Poorly executed strategic decisions can have negative consequences that take a long time to recover from, resulting in lost profits and customer dissatisfaction
Strategic decisions provide direction for the organization and help to ensure that all operational decisions are in line with the overall mission and goals.
Strategic Decision and Operational Decision: The Pro of Providing Direction and Alignment
In the realm of decision-making, strategic decisions and operational decisions serve distinct purposes within an organization. One significant advantage of strategic decisions is their ability to provide direction and ensure alignment with the overall mission and goals of the organization.
When top-level executives or senior management make strategic decisions, they take into account various factors such as market trends, competitor analysis, and customer demands. These decisions establish the long-term vision for the organization, defining its path to success. By setting clear objectives and priorities, strategic decisions create a roadmap that guides all subsequent operational decisions.
Operational decisions, made by middle-level or lower-level managers, focus on day-to-day activities aimed at achieving short-term objectives. These decisions are directly influenced by the strategic direction set by top-level management. By aligning operational decisions with the broader strategy, organizations can ensure that every action taken at the operational level contributes to the achievement of overarching goals.
The advantage of this alignment between strategic and operational decision-making lies in its ability to create a cohesive organizational structure. When all operational decisions are in line with the strategic vision, it reduces ambiguity and confusion among employees. Everyone within the organization understands their role in achieving the larger mission and can work towards common objectives.
Furthermore, this alignment allows for efficient resource allocation. Strategic decisions determine where resources should be allocated to support long-term goals. Operational decisions then optimize resource utilization on a day-to-day basis to achieve those goals effectively. This coordination ensures that resources are not wasted or misused but rather directed towards activities that contribute directly to organizational success.
Additionally, when operational decisions are aligned with strategic goals, it enhances overall organizational performance. Every action taken at the operational level becomes purposeful and meaningful in driving progress towards desired outcomes. The collective efforts of individuals working towards aligned objectives create synergy within an organization, leading to improved productivity and results.
In conclusion, one pro of strategic decisions is their ability to provide direction and alignment for an organization. By setting a clear vision and goals, strategic decisions ensure that all subsequent operational decisions are in line with the overall mission. This alignment not only creates a cohesive organizational structure but also optimizes resource allocation and enhances overall performance. It is through this integration of strategic and operational decision-making that organizations can effectively navigate towards success.
Strategic decisions focus on long-term objectives, allowing for more planning time and better risk management.
Strategic decisions focus on long-term objectives, allowing for more planning time and better risk management. This is a significant advantage that strategic decision-making offers to organizations.
When making strategic decisions, managers have the opportunity to analyze the external environment, assess market trends, and evaluate potential risks and opportunities. This process allows them to take a holistic view of the organization’s long-term goals and develop a comprehensive plan to achieve them. By focusing on long-term objectives, strategic decisions provide a roadmap for the future, ensuring that the organization moves in the right direction.
One of the key benefits of strategic decision-making is the ability to allocate resources effectively. With a clear understanding of long-term objectives, managers can allocate resources in a way that supports those goals. This includes financial resources, human capital, technology investments, and other critical assets. By aligning resource allocation with long-term objectives, organizations can optimize their operations and maximize their chances of success.
Moreover, strategic decisions provide ample time for planning and preparation. Managers can engage in thorough analysis, gather relevant data, consult with experts or stakeholders, and carefully consider different options before making a decision. This planning phase allows organizations to anticipate potential challenges or obstacles that may arise along the way and develop contingency plans to mitigate risks. With adequate planning time, organizations can make informed decisions that minimize uncertainties and increase their chances of success.
Another advantage of strategic decision-making is improved risk management. By focusing on long-term objectives, managers can identify potential risks early on and implement proactive measures to address them. They can assess various scenarios and consider alternative strategies that may help mitigate risks or capitalize on emerging opportunities. Strategic decision-making enables organizations to be proactive rather than reactive when it comes to managing risks.
In conclusion, strategic decisions offer several advantages including the ability to focus on long-term objectives, providing more planning time and better risk management capabilities. By taking a holistic approach towards decision-making and considering long-term goals, organizations can allocate resources effectively, plan ahead, and manage risks more efficiently. Strategic decision-making sets the foundation for success and enables organizations to navigate the complexities of today’s business environment with clarity and purpose.
Strategic decisions allow organizations to be proactive rather than reactive, helping them to anticipate changes in the environment or market conditions.
Strategic decisions allow organizations to be proactive rather than reactive, helping them to anticipate changes in the environment or market conditions. This is a significant advantage that strategic decision-making brings to an organization.
By making strategic decisions, organizations can assess the current state of their industry, identify potential challenges or opportunities, and develop a plan of action accordingly. This proactive approach enables them to stay ahead of the curve and adapt to changing circumstances effectively.
Anticipating changes in the environment or market conditions allows organizations to be prepared for potential disruptions. They can allocate resources strategically, invest in research and development, and explore new avenues for growth before the competition does. This gives them a competitive edge and positions them as industry leaders.
Moreover, strategic decisions help organizations mitigate risks by identifying potential threats early on. By analyzing market trends and consumer behavior patterns, they can make informed choices that minimize potential negative impacts on their operations. This foresight enables them to develop contingency plans and alternative strategies, reducing the likelihood of being caught off guard.
Furthermore, strategic decision-making promotes innovation within an organization. By proactively seeking new opportunities and exploring different paths, organizations can foster a culture of creativity and experimentation. They can invest in new technologies, explore emerging markets, or diversify their product offerings based on strategic insights. This proactive mindset encourages continuous improvement and drives organizational growth.
In contrast, relying solely on operational decision-making without a solid strategic foundation may lead to reactive decision-making. Organizations may find themselves constantly playing catch-up with market trends or struggling to respond effectively to sudden changes in customer demands or technological advancements.
In conclusion, the ability of strategic decisions to enable organizations to be proactive rather than reactive is a valuable advantage. It allows organizations to anticipate changes in the environment or market conditions, make informed choices ahead of time, mitigate risks more effectively, foster innovation, and maintain a competitive edge. By incorporating proactive strategic decision-making into their operations, organizations position themselves for long-term success and sustainable growth.
Strategic decisions can result in greater efficiency since they tend to involve fewer resources and less complexity than operational decisions do.
The Pro of Strategic Decision and Operational Decision: Greater Efficiency
One of the key advantages of strategic decisions over operational decisions is their potential to drive greater efficiency within an organization. Strategic decisions typically involve fewer resources and less complexity compared to operational decisions, allowing for streamlined processes and improved resource allocation.
When making strategic decisions, organizations focus on long-term planning, setting goals, and allocating resources strategically. By carefully considering factors such as market trends, competition, and customer demands, strategic decision-makers can identify opportunities to optimize resource utilization. This means that fewer resources may be required to achieve desired outcomes.
Moreover, strategic decisions often involve setting clear priorities and eliminating unnecessary complexities. By defining a focused strategy, organizations can streamline operations and reduce wasteful activities. This enables them to allocate resources more efficiently towards areas that align with their long-term objectives.
On the other hand, operational decisions tend to be more intricate as they deal with day-to-day activities within an organization. These decisions require immediate attention and often involve managing multiple variables simultaneously. Operational decision-makers must consider factors such as production targets, supply chain logistics, staffing requirements, customer service issues, and quality control measures.
Due to the nature of operational decision-making, it can sometimes be challenging to achieve optimal efficiency. However, by leveraging the strategic decisions made at a higher level within the organization, operational decision-makers can align their actions with the broader objectives set by senior management. This alignment ensures that resources are allocated effectively at the operational level while maintaining focus on achieving strategic goals.
By combining well-planned strategic decisions with efficient operational decision-making processes, organizations can enhance overall efficiency throughout their operations. They can optimize resource utilization while minimizing unnecessary complexities that may hinder productivity.
In conclusion, one significant advantage of strategic decision-making is its potential for greater efficiency compared to operational decision-making. Strategic decisions involve fewer resources and less complexity since they focus on long-term planning and goal-setting. By streamlining processes and aligning operational decisions with strategic objectives, organizations can achieve optimal resource utilization and enhance overall efficiency. This advantage allows organizations to make the most of their available resources and maximize their potential for success.
Operational decisions are made quickly, often with limited information available at the time of decision making, which helps organizations respond quickly to changing conditions or opportunities in their environment or market place.
The Advantage of Operational Decisions: Agility in a Changing World
In today’s fast-paced and dynamic business environment, organizations need to be agile and responsive to stay competitive. One advantage of operational decisions is their ability to be made quickly, even with limited information available at the time. This agility allows organizations to respond promptly to changing conditions or seize opportunities in their environment or marketplace.
Operational decisions are those made on a day-to-day basis, focusing on the execution of strategies set by top-level management. These decisions deal with routine activities and operational processes within an organization. Unlike strategic decisions that require extensive analysis and planning, operational decisions often need to be made swiftly due to the urgent nature of the situation.
The ability to make quick operational decisions is particularly valuable when faced with rapidly changing market conditions, emerging trends, or unexpected events. In these situations, waiting for comprehensive information or conducting lengthy analyses may lead to missed opportunities or falling behind competitors.
By making operational decisions promptly, organizations can adapt their operations in response to market shifts or capitalize on sudden opportunities. This agility enables them to stay ahead of the curve and maintain a competitive edge. Whether it’s adjusting production schedules, reallocating resources, modifying marketing campaigns, or responding to customer demands, the ability to make rapid operational decisions ensures that organizations can navigate through uncertainty effectively.
Furthermore, quick decision-making in operations helps organizations maintain flexibility and responsiveness. The ability to adapt swiftly allows businesses to address customer needs promptly and efficiently. It also enables them to optimize internal processes and react proactively to changes in supply chain dynamics or manufacturing requirements.
However, it’s important to note that while speed is advantageous in making operational decisions, it should not compromise the accuracy or quality of those decisions. Even though there might be limited information available initially, it is crucial for decision-makers to rely on relevant data and experience-based insights whenever possible.
In conclusion, one significant pro of operational decision-making is its speed and agility. Making quick decisions, even with limited information, allows organizations to respond promptly to changing conditions or seize opportunities in their environment or marketplace. By embracing this advantage, organizations can navigate through uncertainties effectively and maintain their competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business world.
Operational decisions enable organizations to take advantage of short-term opportunities that may not fit into a strategic plan but could still benefit the organization’s overall goals and objectives over time.
Operational decisions enable organizations to seize short-term opportunities that may not align with the long-term strategic plan but can still contribute to the organization’s overall goals and objectives in the long run. While strategic decisions focus on the big picture and set the course for the future, operational decisions allow organizations to adapt and respond quickly to immediate opportunities that arise.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, it is crucial for organizations to be agile and flexible. Operational decisions provide the necessary agility by allowing managers to capitalize on unexpected opportunities that may have a positive impact on the organization’s growth and success. These opportunities could include a sudden surge in customer demand, a competitor’s failure, or emerging market trends.
By making operational decisions that seize these short-term opportunities, organizations can gain a competitive advantage and enhance their market position. While these opportunities may not fit into the long-term strategic plan initially, they can still contribute significantly to achieving the organization’s overall goals over time.
Additionally, operational decisions enable organizations to test new ideas and strategies on a smaller scale before incorporating them into the long-term strategic plan. By experimenting with different approaches through operational decision-making, organizations can gather valuable insights and data that inform future strategic decisions.
Furthermore, taking advantage of short-term opportunities through operational decision-making can boost employee morale and motivation. When employees see their ideas being implemented quickly and yielding positive results, it fosters a sense of empowerment and encourages innovative thinking throughout the organization.
However, it is important to strike a balance between seizing short-term opportunities through operational decision-making and staying aligned with the long-term strategic direction. Organizations should evaluate these opportunities carefully to ensure they are consistent with their core values, brand image, and overall objectives.
In conclusion, operational decisions play a vital role in enabling organizations to capitalize on short-term opportunities that may not initially align with their long-term strategic plan but have potential benefits over time. By embracing agility and flexibility in decision-making processes, organizations can adapt to changing circumstances, gain a competitive edge, and continuously evolve towards their overarching goals.
Operational decision making is usually less costly than strategic decision making due to its shorter timeline and more focused scope of analysis needed for each decision made within it’s shorter timeframe .
Operational Decision Making: A Cost-Effective Approach
When it comes to decision making in organizations, both strategic decisions and operational decisions play a vital role. While strategic decisions shape the long-term direction of an organization, operational decisions focus on the day-to-day activities that support the overall strategy. One significant advantage of operational decision making is its cost-effectiveness compared to strategic decision making.
Operational decision making is usually less costly due to its shorter timeline and more focused scope of analysis needed for each decision made within its shorter timeframe. Strategic decisions often require extensive research, market analysis, and consultation with various stakeholders. These processes can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, leading to higher costs associated with gathering data, conducting market research, and seeking expert advice.
In contrast, operational decisions typically have a shorter timeline as they deal with immediate or short-term objectives. The scope of analysis required for operational decisions is more focused and specific to the particular situation at hand. This narrow focus allows managers to gather relevant information quickly and make informed decisions without requiring extensive research or involving multiple stakeholders.
The reduced time and resources needed for operational decision making contribute to cost savings for organizations. With quicker turnaround times, managers can address pressing issues promptly, ensuring smooth operations and minimizing potential disruptions. By focusing on immediate goals within a limited scope, organizations can allocate their resources efficiently without unnecessary expenditures on lengthy research or consultations.
Moreover, the cost-effectiveness of operational decision making extends beyond financial considerations. It also allows organizations to be more agile and responsive in their day-to-day operations. Rapid decision-making enables them to adapt swiftly to changing market dynamics or emerging opportunities while maintaining a competitive edge.
However, it’s important to note that while operational decision making may be less costly in terms of resources and time compared to strategic decision making, both are essential for organizational success. Strategic decisions provide the overall vision and direction for an organization’s growth and sustainability. Operational decisions ensure effective execution of the strategy and help achieve short-term goals that contribute to the long-term vision.
In conclusion, operational decision making offers a cost-effective approach for organizations. Its shorter timeline and focused scope of analysis allow for quicker, more efficient decision-making processes. By saving time and resources, organizations can allocate their valuable assets effectively and respond promptly to operational challenges. However, it is crucial to strike a balance between strategic decision making and operational decision making to ensure long-term success and sustainability.
Operational decision making allows managers more flexibility when responding quickly to new challenges or situations as they arise without having to wait for approval from higher levels of management within an organization .
Operational Decision Making: Empowering Managers with Flexibility and Agility
One significant advantage of operational decision making is the ability it provides managers to respond quickly to new challenges or situations as they arise. Unlike strategic decisions that often require approval from higher levels of management, operational decisions grant managers the flexibility to make necessary adjustments on the ground without delay.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations face constant changes and unexpected circumstances that demand swift action. Operational decision making empowers managers to adapt and address these challenges promptly, without being hindered by bureaucratic processes or waiting for approval from higher-ups.
When managers have the autonomy to make operational decisions, they can seize opportunities and tackle problems in real-time. This flexibility allows them to respond swiftly to market fluctuations, customer demands, or unforeseen events that may impact day-to-day operations. By eliminating unnecessary layers of approval, operational decision making streamlines the decision-making process and enables organizations to stay agile in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Moreover, this pro of operational decision making fosters a sense of ownership among managers. When they are trusted with the authority to make decisions within their domain, they feel more accountable for the outcomes. This accountability drives them towards taking calculated risks and finding innovative solutions that can propel the organization forward.
Operational decision making also promotes efficient communication within an organization. With decentralized decision-making authority, information can flow more freely between different levels of management. Managers at lower levels have firsthand knowledge of ground-level operations and customer feedback, allowing them to make informed decisions based on real-time data. This open communication enhances collaboration and enables organizations to adapt swiftly in response to changing market dynamics.
However, it is important to note that while operational decision making offers flexibility and agility, it should still align with the overall strategic direction set by top-level executives. The balance between strategic decisions and operational decisions ensures that actions taken at the ground level contribute effectively towards achieving long-term organizational goals.
In conclusion, operational decision making provides managers with the flexibility and autonomy to respond quickly to new challenges or situations as they arise. By eliminating bureaucratic hurdles and empowering managers with decision-making authority, organizations can adapt swiftly in a dynamic business environment. This not only enhances their ability to seize opportunities but also fosters a culture of ownership and accountability. Embracing operational decision making as a proactively responsive approach can be a key driver of success in today’s ever-changing marketplace.
Operational decision making enables managers at lower levels of an organization have autonomy over certain aspects of their job responsibilities which can lead increased motivation among employees due its empowering nature
Operational Decision Making: Empowering Autonomy and Increasing Motivation
Operational decision making within an organization offers a significant advantage by empowering managers at lower levels to have autonomy over certain aspects of their job responsibilities. This autonomy can lead to increased motivation among employees, ultimately benefiting the organization as a whole.
When managers are given the freedom to make operational decisions, they feel a sense of ownership and control over their work. This empowerment allows them to take charge of their responsibilities, make independent choices, and have a direct impact on the outcomes they produce. As a result, managers become more engaged and motivated in their roles.
By granting autonomy in operational decision making, organizations foster a culture of trust and respect. Employees feel valued when their opinions and expertise are recognized and incorporated into decision-making processes. This sense of empowerment not only motivates individuals to perform better but also encourages them to take initiative, think creatively, and contribute innovative ideas that can drive organizational success.
Furthermore, operational decision making enhances the development of managerial skills at lower levels within the organization. When managers are given the opportunity to make decisions related to their specific areas of responsibility, they gain valuable experience in problem-solving, critical thinking, and decision analysis. This not only strengthens their skill set but also prepares them for future leadership roles within the organization.
Additionally, empowering employees through operational decision making can lead to improved collaboration and teamwork. When individuals have autonomy over certain aspects of their work, they are more likely to collaborate with colleagues across different departments or functions. This collaboration fosters knowledge sharing, cross-functional understanding, and synergy among teams – all contributing factors for achieving organizational goals efficiently.
In conclusion, operational decision making offers a pro that cannot be overlooked: it empowers managers at lower levels by granting them autonomy over certain aspects of their job responsibilities. This empowerment leads to increased motivation among employees as they feel valued and recognized for their contributions. Moreover, it enhances skill development while promoting collaboration and teamwork within the organization. By embracing operational decision making, organizations can create a positive work environment that drives employee engagement and ultimately contributes to their overall success.
Strategic decisions can be costly and time consuming as they require a lot of research, analysis, and planning.
The Costly and Time-Consuming Nature of Strategic Decisions
Strategic decisions are pivotal in shaping the long-term success of an organization. However, it is important to acknowledge that these decisions come with their own set of challenges. One significant drawback is the inherent cost and time required to make well-informed strategic decisions.
When it comes to strategic decision-making, organizations must invest considerable resources into research, analysis, and planning. This often involves gathering market data, conducting competitor analysis, assessing technological advancements, and evaluating customer trends. These processes demand extensive research efforts to gain a comprehensive understanding of the external environment and industry dynamics.
Moreover, strategic decisions require thorough analysis to evaluate different options and potential outcomes. This entails examining various scenarios, conducting feasibility studies, and weighing the risks associated with each decision. The complexity involved in this analytical process can be time-consuming as decision-makers strive to make informed choices that align with the organization’s objectives.
Furthermore, strategic decisions necessitate meticulous planning to ensure effective implementation. Developing a detailed action plan that outlines the steps required for successful execution is crucial. This planning phase involves setting priorities, allocating resources appropriately, defining timelines, and establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress towards desired outcomes.
All these factors contribute to the overall cost and time investment associated with strategic decision-making. Organizations must allocate budgetary resources for research activities, hire experts or consultants if needed, invest in technology or tools for data analysis, and dedicate substantial managerial time towards the decision-making process.
Despite these challenges, it is essential for organizations to recognize the importance of making well-thought-out strategic decisions. While they may be costly and time-consuming upfront, strategic decisions have the potential to shape an organization’s future success by enabling it to adapt to changing market conditions or gain a competitive edge.
To mitigate these drawbacks, organizations can streamline their decision-making processes by leveraging technology-driven solutions for data gathering and analysis. Additionally, involving cross-functional teams and encouraging collaboration can help distribute the workload and facilitate a more efficient decision-making process.
In conclusion, the cost and time required for strategic decision-making should not be overlooked. It is crucial for organizations to allocate sufficient resources, both financial and human, to conduct thorough research, analysis, and planning. While the process may be demanding, making well-informed strategic decisions is an investment in an organization’s long-term success.
Strategic decisions may not always provide immediate results or feedback on the effectiveness of the decision taken.
The Con of Strategic Decision and Operational Decision: Delayed Feedback on Effectiveness
Strategic decisions are often made with the intention of achieving long-term goals and gaining a competitive edge in the market. While these decisions are crucial for an organization’s success, one con to consider is that they may not always provide immediate results or feedback on their effectiveness.
Unlike operational decisions that deal with day-to-day activities and yield more tangible and immediate outcomes, strategic decisions involve setting a course for the future. This means that it may take time before the impact of a strategic decision becomes apparent or measurable.
For example, if a company decides to invest heavily in research and development to develop innovative products, it may take several months or even years before those products are ready for market launch. During this time, there might be limited feedback on whether the strategic decision was effective in achieving its intended outcomes.
Similarly, if an organization decides to enter a new market or expand its operations internationally, it can take time to establish a foothold and gain traction. The success of such strategic decisions may not be evident until after significant investments have been made and sufficient time has passed to evaluate their impact.
This delay in feedback on the effectiveness of strategic decisions can be challenging for organizations as they need to wait patiently before assessing whether their chosen strategies are yielding desired results. It requires managers and decision-makers to have a long-term perspective and trust in the strategic direction they have set.
To mitigate this con, organizations can implement monitoring mechanisms and performance indicators that allow them to track progress towards their strategic goals. Regular evaluations can provide insights into whether adjustments need to be made or if the chosen strategies are still aligned with changing market conditions.
While delayed feedback may pose challenges, it is important to remember that strategic decisions are often made with long-term benefits in mind. They set the foundation for growth and sustainability, even if immediate results might not be readily apparent. By carefully monitoring progress and adapting strategies as needed, organizations can navigate through this con and ensure that their strategic decisions ultimately lead to success.
Operational decisions are often made quickly and without adequate consideration of long-term implications or impacts on other areas of the business.
The Pitfall of Operational Decisions: Neglecting Long-Term Implications
Operational decisions are the lifeblood of day-to-day business operations. They ensure that tasks are carried out efficiently, resources are managed effectively, and customer demands are met promptly. However, there is a potential downside to the speed and immediacy of operational decision-making: the tendency to overlook long-term implications and impacts on other areas of the business.
In the fast-paced nature of operational decision-making, managers often face time constraints and pressure to resolve immediate issues. This can lead to a myopic focus on short-term gains or solving immediate problems without considering the broader consequences. While these decisions may seem beneficial in the moment, they can have unintended consequences that ripple through the organization in the long run.
One common pitfall is neglecting to assess how an operational decision might impact other departments or functions within the organization. For example, a decision made by a production manager to increase production output may seem like a positive move for meeting customer demand. However, if this decision is not coordinated with other departments such as procurement or logistics, it could lead to inventory stockouts or strain on the supply chain.
Similarly, operational decisions made without adequate consideration of long-term implications can result in suboptimal resource allocation. For instance, a marketing manager might decide to aggressively discount products to boost short-term sales figures without considering the potential impact on brand perception or profitability in the long term.
Furthermore, hastily made operational decisions can hinder adaptability and flexibility within an organization. By focusing solely on immediate needs, managers may fail to identify emerging trends or anticipate future challenges. This lack of foresight can leave organizations ill-prepared for changes in customer preferences, market dynamics, or technological advancements.
To mitigate this conundrum, organizations should strive for a balance between speed and thoughtful consideration when making operational decisions. Managers should take a step back and evaluate how their choices align with broader organizational goals, strategies, and values. They should also foster cross-departmental collaboration and communication to ensure that operational decisions are coordinated and aligned with the overall business objectives.
In conclusion, while operational decisions are necessary for day-to-day business operations, it is vital to avoid the pitfall of neglecting long-term implications. Hastily made decisions can have unintended consequences and hinder an organization’s ability to adapt and thrive in a dynamic environment. By incorporating a more holistic and forward-thinking approach to operational decision-making, organizations can navigate potential pitfalls and enhance their overall effectiveness in achieving long-term success.
Operational decisions can lead to an increase in operational costs if not properly managed or monitored over time.
Operational decisions can lead to an increase in operational costs if not properly managed or monitored over time. While operational decisions are essential for the day-to-day functioning of an organization, they can have financial implications if not handled efficiently.
One of the main reasons operational decisions can result in increased costs is when there is a lack of proper monitoring and control. Without regular evaluation and analysis of operational processes, inefficiencies may go unnoticed, leading to unnecessary expenses. For example, if inventory levels are not closely monitored, it can result in overstocking or stockouts, both of which can impact the bottom line.
Moreover, poor decision-making regarding resource allocation can also contribute to increased costs. When resources such as labor, equipment, or materials are not allocated optimally, it can lead to inefficiencies and wastage. For instance, improper scheduling of employee shifts may result in unnecessary overtime expenses or underutilization of staff.
In addition, inadequate risk management in operational decision-making can lead to unexpected costs. Failure to identify and mitigate potential risks within operations can result in disruptions or emergencies that require immediate action and additional expenditures. For instance, not having contingency plans for equipment breakdowns may lead to costly repairs or production delays.
Furthermore, outdated technology or inefficient processes can also contribute to increased operational costs. Failing to invest in modern technology or neglecting process improvements may hinder productivity and increase expenses. For example, using outdated machinery that consumes more energy than newer models could significantly impact utility bills.
To mitigate these cost-related challenges associated with operational decisions, organizations should prioritize effective monitoring systems and regular performance evaluations. Implementing robust control mechanisms helps identify areas where costs are escalating and allows for timely corrective actions.
Investing in training programs for employees involved in making operational decisions is also crucial. By equipping them with the necessary knowledge and skills to analyze data effectively and make informed choices, organizations can minimize cost-related risks arising from poor decision-making.
Lastly, embracing technology and process improvements can streamline operations, reduce waste, and optimize resource allocation. Regularly reviewing and updating operational processes ensures that they remain efficient and cost-effective.
In conclusion, while operational decisions are necessary for the day-to-day functioning of an organization, they can lead to increased costs if not properly managed or monitored. By implementing effective monitoring systems, investing in employee training, and embracing technology and process improvements, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with operational decision-making, thereby reducing unnecessary expenses and improving overall efficiency.
Strategic decisions can be difficult to reverse once implemented due to their complexity and far reaching implications for the business as a whole.
Con of Strategic Decision and Operational Decision: Difficulty in Reversal
Strategic decisions are often complex and have far-reaching implications for a business. Once implemented, they can be challenging to reverse, leading to potential drawbacks for organizations. This con highlights the importance of careful consideration and thorough analysis before making strategic decisions.
One of the main reasons why strategic decisions are difficult to reverse is their complexity. These decisions involve considering various factors such as market trends, competitor analysis, financial projections, and long-term goals. The intricate nature of strategic decision-making requires extensive research, consultation with experts, and evaluation of multiple scenarios. Once a decision is made and implemented, it can be challenging to undo or change course without significant disruptions.
Moreover, strategic decisions often have broad implications for the entire business. They impact various departments, functions, and stakeholders within an organization. Changes resulting from strategic decisions may require realignment of resources, restructuring of processes, or even changes in the organizational culture. Reversing these changes can disrupt operations and create confusion among employees.
Another factor contributing to the difficulty in reversing strategic decisions is the investment involved. Strategic decisions often require substantial financial resources and time commitments. Investments in research and development, infrastructure development, or expansion into new markets can be costly endeavors. Reversing these decisions would mean wasting valuable resources that were initially allocated.
Furthermore, strategic decisions are interconnected with numerous other business activities and initiatives. Changing one aspect of a strategic decision might have ripple effects on other areas within the organization. This interdependency makes it challenging to reverse a decision without causing unintended consequences or disruptions elsewhere.
To mitigate this con, organizations should prioritize thorough analysis and evaluation during the strategic decision-making process. It is crucial to consider potential risks, conduct feasibility studies, scenario planning exercises, and engage key stakeholders early on. By taking a proactive approach to decision-making, organizations can reduce the likelihood of needing reversals in the first place.
In conclusion, the difficulty in reversing strategic decisions is a significant con that organizations must consider. The complexity, far-reaching implications, and investment involved make reversals challenging and disruptive. By recognizing this con and implementing robust decision-making processes, organizations can minimize the need for reversals and ensure that strategic decisions align with their long-term objectives.
Poorly executed strategic decisions can have negative consequences that take a long time to recover from, resulting in lost profits and customer dissatisfaction
The Consequence of Poorly Executed Strategic Decisions: Lost Profits and Customer Dissatisfaction
Strategic decisions are the backbone of an organization’s long-term success. They set the direction, allocate resources, and determine the competitive advantage. However, when these strategic decisions are poorly executed, they can have severe consequences that take a long time to recover from.
One of the most significant drawbacks of a poorly executed strategic decision is the potential loss of profits. When a strategic decision fails to deliver the desired outcomes or fails to adapt to changing market conditions, it can lead to financial setbacks. For example, investing in a new product line without conducting thorough market research or misjudging customer demand can result in low sales and wasted resources. This can directly impact revenue and profitability.
Moreover, poorly executed strategic decisions often lead to customer dissatisfaction. Customers are at the heart of any business, and when strategic decisions fail to meet their needs or expectations, it can result in lost trust and loyalty. For instance, if a company decides to cut costs by reducing customer service staff without considering the impact on service quality, customers may experience longer wait times or inadequate support. This can lead to negative reviews, decreased customer retention rates, and ultimately damage the company’s reputation.
Recovering from these negative consequences can be a lengthy process. It often requires revisiting the initial decision-making process, identifying where things went wrong, and implementing corrective measures. This not only takes time but also involves additional costs for course correction. The organization may need to invest in new strategies or initiatives to regain lost profits and rebuild customer trust.
To mitigate these risks associated with poorly executed strategic decisions, organizations must prioritize careful planning and execution. Thorough research and analysis should be conducted before making any major decision. It is crucial to consider various scenarios and potential outcomes while involving key stakeholders for diverse perspectives.
Regular monitoring and evaluation are also essential during implementation to identify early signs of deviation from the desired results. This allows for timely adjustments and corrective actions to minimize the negative impact.
In conclusion, poorly executed strategic decisions can lead to lost profits and customer dissatisfaction. Recovering from these consequences can be challenging and time-consuming. To avoid such pitfalls, organizations must prioritize effective execution, continuous monitoring, and a customer-centric approach when making strategic decisions. By doing so, they can enhance their chances of long-term success and maintain a positive reputation in the market.