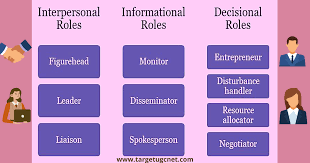
Managerial Decision Making Techniques: Enhancing Organizational Success
In the dynamic and competitive business environment, effective decision making is crucial for managerial success. Managers play a pivotal role in steering organizations towards their goals, and their ability to make sound decisions can greatly impact overall performance. To navigate the complexities of decision making, managers employ various techniques that enhance their analytical skills and facilitate informed choices. In this article, we will explore some commonly used managerial decision making techniques.
Rational Decision Making:
Rational decision making is a systematic approach that involves gathering relevant information, evaluating alternatives, and selecting the most optimal solution based on logical reasoning. This technique follows a step-by-step process, including identifying the problem, generating alternatives, evaluating pros and cons, selecting the best option, and implementing it. By relying on data-driven analysis and objective evaluation, managers can minimize biases and make informed decisions.
Intuitive Decision Making:
Intuition plays a significant role in managerial decision making when faced with time constraints or complex situations where limited information is available. Intuitive decision making relies on experience, gut feelings, and pattern recognition to arrive at quick decisions. While it may seem subjective compared to rational decision making, intuition can be honed through years of experience and exposure to similar scenarios.
SWOT Analysis:
SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is a widely used technique for strategic decision making. It involves assessing internal strengths and weaknesses of an organization along with external opportunities and threats in its operating environment. By conducting a SWOT analysis, managers can gain valuable insights into their organization’s current position and identify areas where strategic decisions can be made to capitalize on strengths or mitigate weaknesses.
Cost-Benefit Analysis:
When faced with multiple alternatives or investment decisions, managers often use cost-benefit analysis as a tool to evaluate potential outcomes against associated costs. This technique quantifies both tangible and intangible factors, allowing managers to make decisions that maximize benefits while minimizing costs. By assigning values to various factors and weighing them against each other, managers can objectively assess the potential return on investment.
Decision Trees:
Decision trees are visual representations of decision-making processes that help managers evaluate alternative paths and potential outcomes. By mapping out different scenarios and their associated probabilities, decision trees provide a structured framework for analyzing complex decisions. This technique allows managers to consider multiple variables and their interdependencies, aiding in identifying the most favorable course of action.
Group Decision Making:
In situations where multiple stakeholders or team members are involved, group decision making techniques can be employed to ensure inclusivity and collective input. Techniques such as brainstorming, nominal group technique, or Delphi method encourage active participation, idea generation, and consensus building among team members. By leveraging the diverse perspectives and expertise of the group, managers can arrive at more robust decisions.
Successful managerial decision making requires a combination of analytical thinking, strategic foresight, and effective communication skills. While these techniques offer valuable frameworks for decision making, it is important for managers to adapt them based on the specific context and nature of the problem at hand.
By adopting these techniques and continuously refining their decision-making skills, managers can enhance organizational success by making informed choices that align with strategic objectives. Ultimately, effective managerial decision making not only drives performance but also fosters a culture of accountability and innovation within an organization.
Exploring Frequently Asked Questions about Managerial Decision-Making Techniques
- What is the techniques of decision-making?
- What are 4 decision-making techniques?
- What are the five decision-making techniques?
- What are the 7 decision-making strategies?
What is the techniques of decision-making?
There are several techniques commonly used in decision-making processes. Here are some of the key techniques:
- Rational Decision Making: This technique involves a systematic approach to decision making, where managers gather relevant information, evaluate alternatives, and select the most optimal solution based on logical reasoning.
- Intuitive Decision Making: Intuition plays a role when faced with time constraints or complex situations with limited information. Managers rely on their experience, gut feelings, and pattern recognition to make quick decisions.
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is a technique used for strategic decision making. It involves assessing internal strengths and weaknesses of an organization along with external opportunities and threats in its operating environment.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: This technique evaluates potential outcomes against associated costs. It helps managers objectively assess the potential return on investment by assigning values to various factors and weighing them against each other.
- Decision Trees: Decision trees are visual representations of decision-making processes that help managers evaluate alternative paths and potential outcomes. They provide a structured framework for analyzing complex decisions by mapping out different scenarios and their associated probabilities.
- Group Decision Making: Involving multiple stakeholders or team members can be achieved through techniques such as brainstorming, nominal group technique, or Delphi method. These techniques encourage active participation, idea generation, and consensus building among team members.
- Pareto Analysis: Also known as the 80/20 rule, Pareto analysis helps identify the most significant factors contributing to a problem or goal achievement by focusing on the vital few (20%) rather than the trivial many (80%).
- Six Thinking Hats: This technique encourages different perspectives by assigning specific roles or “hats” to participants during discussions or decision-making processes. Each hat represents a different thinking style (e.g., analytical thinking, emotional thinking) to ensure comprehensive exploration of ideas.
- Scenario Analysis: This technique involves creating multiple scenarios based on different assumptions or variables. It helps managers anticipate potential outcomes and make decisions that consider a range of possible future situations.
- Decision Matrix: A decision matrix is a tool that allows managers to evaluate alternatives against multiple criteria. By assigning weights to different criteria and scoring each alternative, managers can objectively compare options and select the most suitable one.
These techniques provide frameworks and tools to support decision-making processes. Managers can adapt and combine these techniques based on the specific context, problem complexity, and available resources to make informed choices.
What are 4 decision-making techniques?
There are numerous decision-making techniques available, but here are four commonly used ones:
- Rational Decision Making: This technique involves a systematic approach that includes identifying the problem, gathering relevant information, evaluating alternatives, and selecting the most optimal solution based on logical reasoning. It relies on data-driven analysis and objective evaluation to minimize biases and make informed decisions.
- Intuitive Decision Making: Intuition plays a role in decision making when faced with time constraints or situations where limited information is available. It relies on experience, gut feelings, and pattern recognition to arrive at quick decisions. While it may seem subjective compared to rational decision making, intuition can be honed through experience and exposure to similar scenarios.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: This technique is useful when evaluating multiple alternatives or investment decisions. It involves assessing the potential outcomes against associated costs. By quantifying both tangible and intangible factors and weighing them against each other, managers can objectively assess the potential return on investment.
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is a strategic decision-making technique that involves assessing an organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses along with external opportunities and threats in its operating environment. By conducting a SWOT analysis, managers can gain valuable insights into their organization’s current position and identify areas where strategic decisions can be made to capitalize on strengths or mitigate weaknesses.
These techniques provide frameworks for making informed decisions across different contexts and help managers consider various factors before arriving at the best course of action.
What are the five decision-making techniques?
There are numerous decision-making techniques that individuals and organizations can employ. While it’s challenging to narrow them down to just five, here are five commonly used techniques:
- Rational Decision Making: This technique involves a systematic approach to decision making, where information is gathered, alternatives are evaluated, and the most optimal solution is selected based on logical reasoning and analysis.
- Intuitive Decision Making: Intuition plays a role when time constraints or limited information are present. It relies on experience, gut feelings, and pattern recognition to arrive at quick decisions.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: This technique involves evaluating potential outcomes against associated costs. By quantifying both tangible and intangible factors, decision makers can objectively assess the potential return on investment.
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is used for strategic decision making. It involves assessing internal strengths and weaknesses of an organization along with external opportunities and threats in its operating environment.
- Decision Trees: Decision trees are visual representations of decision-making processes that help evaluate alternative paths and potential outcomes. By mapping out different scenarios and their associated probabilities, decision trees provide a structured framework for analyzing complex decisions.
Remember that these techniques serve as frameworks to guide the decision-making process but should be adapted based on the specific context and nature of the problem at hand.
What are the 7 decision-making strategies?
There are several decision-making strategies that individuals and organizations can employ. While the specific number and categorization may vary, here are seven commonly recognized decision-making strategies:
- Rational Decision Making: This strategy involves a systematic approach, where decisions are made based on logical reasoning, data analysis, and evaluation of alternatives. It follows a step-by-step process to ensure informed choices.
- Intuitive Decision Making: Intuition plays a significant role in this strategy, relying on gut feelings, experience, and pattern recognition. It is often used in situations where time is limited or when there is incomplete information.
- Incremental Decision Making: This strategy involves making small adjustments or incremental changes over time rather than making large-scale decisions all at once. It allows for flexibility and adaptation as new information becomes available.
- Normative Decision Making: Normative decision making focuses on establishing norms or standards to guide the decision-making process. It involves considering ethical principles, social norms, and organizational values when making choices.
- Satisficing: Satisficing is a strategy where individuals or organizations choose the first acceptable option that meets their minimum criteria rather than striving for the optimal solution. This approach balances time constraints and resources while still achieving satisfactory outcomes.
- Group Decision Making: This strategy involves involving multiple stakeholders or team members in the decision-making process. Techniques such as brainstorming, consensus building, or voting are used to gather diverse perspectives and reach collective decisions.
- Autocratic Decision Making: In this strategy, decision making is centralized with one individual who has the authority to make choices without consulting others extensively. This approach is useful in situations where quick decisions are required or when there is a need for strong leadership.
It’s important to note that these strategies can be used individually or in combination depending on the context of the decision being made and the preferences of individuals or organizations involved.