Strategic Decision Model: A Guide to Making Informed Choices
In today’s fast-paced and competitive world, making strategic decisions is crucial for the success of individuals and organizations alike. Whether you are a business leader, an entrepreneur, or simply someone faced with a significant life choice, having a structured approach to decision-making can greatly increase your chances of achieving your goals. This is where the Strategic Decision Model comes into play.
The Strategic Decision Model is a systematic framework that helps individuals and organizations make informed choices by considering various factors and evaluating potential outcomes. It provides a step-by-step process that guides decision-makers through the complexities of strategic decision-making.
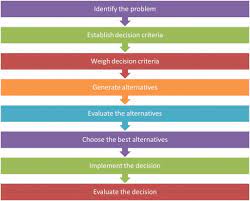
- Define the Problem: The first step in the Strategic Decision Model is to clearly define the problem or opportunity at hand. This involves identifying the desired outcome, understanding the context, and determining what needs to be resolved or achieved.
- Gather Information: Once the problem is defined, it’s essential to gather relevant information from various sources. This includes conducting research, analyzing data, seeking expert opinions, and considering past experiences or case studies. The more comprehensive your information gathering process, the better equipped you will be to make an informed decision.
- Identify Alternatives: In this stage, brainstorm and generate multiple alternatives or solutions to address the problem at hand. Encourage creativity and consider both conventional and unconventional options. Aim for a diverse range of alternatives that cover different approaches or strategies.
- Evaluate Alternatives: Now it’s time to assess each alternative against specific criteria such as feasibility, cost-effectiveness, potential risks, alignment with goals, and potential outcomes. Use quantitative and qualitative analysis techniques to compare alternatives objectively.
- Make a Choice: Based on your evaluation of each alternative, select the one that best aligns with your objectives and has the highest probability of success. Consider any trade-offs or compromises that may be necessary along with their potential consequences.
- Implement Your Decision: Once a choice is made, it’s important to develop an action plan outlining the steps required to implement your decision effectively. Assign responsibilities, set timelines, allocate resources, and establish performance metrics to monitor progress.
- Evaluate and Adapt: After implementation, regularly evaluate the outcomes of your decision. Assess whether the desired results are being achieved and if any adjustments or adaptations are necessary. This step ensures continuous improvement and allows for flexibility in response to changing circumstances.
The Strategic Decision Model provides a structured and systematic approach to decision-making that minimizes biases and maximizes the chances of success. By following this model, individuals and organizations can make more informed choices that align with their goals and aspirations.
Remember, decision-making is an ongoing process, and each decision you make can impact future choices. By embracing a strategic approach to decision-making, you empower yourself with the tools needed to navigate complex challenges and seize opportunities with confidence.
Common Questions About Strategic Decision Models: Explained
- What is a strategic decision model?
- How do you develop a strategic decision model?
- How can a strategic decision model help businesses make better decisions?
- What are the components of a strategic decision model?
- What are the benefits of using a strategic decision model?
- What challenges can arise when using a strategic decision model?
What is a strategic decision model?
A strategic decision model is a systematic framework or approach that helps individuals and organizations make informed choices when faced with complex and significant decisions. It provides a structured process that guides decision-makers through various stages, ensuring that all relevant factors are considered and evaluated before making a final decision.
The purpose of a strategic decision model is to minimize biases, increase objectivity, and improve the overall quality of decision-making. It helps decision-makers think critically, consider multiple perspectives, and weigh the potential outcomes and consequences of their choices.
While there are different variations of strategic decision models, they generally involve several common steps:
- Problem Definition: Clearly define the problem or opportunity that requires a decision. This involves understanding the context, identifying goals or desired outcomes, and determining what needs to be resolved or achieved.
- Information Gathering: Gather relevant information from various sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the situation. This may involve conducting research, analyzing data, seeking expert opinions, and considering past experiences or case studies.
- Alternative Generation: Brainstorm and generate multiple alternatives or solutions to address the problem at hand. Encourage creativity and consider both conventional and unconventional options.
- Evaluation of Alternatives: Assess each alternative against specific criteria such as feasibility, cost-effectiveness, potential risks, alignment with goals, and potential outcomes. Use quantitative and qualitative analysis techniques to compare alternatives objectively.
- Decision Making: Based on the evaluation of each alternative, select the one that best aligns with objectives and has the highest probability of success. Consider any trade-offs or compromises that may be necessary along with their potential consequences.
- Implementation Planning: Develop an action plan outlining the steps required to implement the chosen alternative effectively. Assign responsibilities, set timelines, allocate resources, and establish performance metrics to monitor progress.
- Evaluation and Adaptation: Regularly evaluate the outcomes of the decision implementation process. Assess whether desired results are being achieved and if any adjustments or adaptations are necessary. This step ensures continuous improvement and allows for flexibility in response to changing circumstances.
By following a strategic decision model, individuals and organizations can make more informed choices that consider a wide range of factors, minimize biases, and increase the likelihood of successful outcomes. It provides a structured approach to decision-making that promotes critical thinking and systematic evaluation, leading to better decision quality.
How do you develop a strategic decision model?
Developing a strategic decision model requires careful thought and consideration. Here are some steps to guide you through the process:
- Identify the Purpose: Determine the specific purpose or objective of your strategic decision model. Clarify what types of decisions you want to address and the goals you aim to achieve through this model.
- Understand the Context: Gain a deep understanding of the context in which your decisions will be made. Consider the industry, market conditions, organizational culture, stakeholders’ expectations, and any external factors that may influence decision-making.
- Research Existing Models: Conduct research to explore existing strategic decision models that are relevant to your needs. Analyze their components, processes, and underlying principles. This will provide valuable insights and help you identify elements that can be incorporated into your own model.
- Define Decision-Making Steps: Based on your research and understanding of the context, outline a series of steps or stages that decision-makers should follow when using your strategic decision model. These steps should be logical, sequential, and align with best practices in decision-making.
- Consider Decision Criteria: Determine the key criteria that will guide decision-makers in evaluating alternatives within each step of your model. These criteria could include factors such as feasibility, profitability, risk assessment, market potential, resource allocation, ethical considerations, or any other relevant factors specific to your domain.
- Establish Evaluation Methods: Define appropriate evaluation methods for each criterion identified in the previous step. This could involve creating rating scales, developing scoring systems, using cost-benefit analysis techniques, conducting SWOT analyses (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats), or employing other quantitative or qualitative evaluation methods.
- Incorporate Flexibility: Recognize that decisions often require flexibility due to changing circumstances or new information emerging during the process. Build mechanisms within your model that allow for adaptation and adjustments as needed without compromising its overall structure and effectiveness.
- Test and Refine: Pilot your strategic decision model by applying it to real-life scenarios or hypothetical situations. Gather feedback from decision-makers who use the model and evaluate its effectiveness in guiding their decision-making process. Use this feedback to refine and improve the model as necessary.
- Communicate and Train: Once your strategic decision model is developed and refined, ensure that it is effectively communicated to all relevant stakeholders. Provide training and guidance on how to use the model correctly, emphasizing its benefits and importance in making informed decisions.
- Continuous Improvement: Recognize that a strategic decision model is not a static entity. Encourage ongoing feedback, monitor its usage, and continuously seek opportunities for improvement. Stay updated with emerging trends or changes in your industry that may require adjustments to the model over time.
By following these steps, you can develop a strategic decision model that suits your specific needs and enhances the quality of decision-making within your organization or personal life.
How can a strategic decision model help businesses make better decisions?
A strategic decision model can greatly benefit businesses by providing a structured framework to make better decisions. Here are some ways in which it can help:
- Clarity and Focus: The strategic decision model helps businesses define the problem or opportunity clearly, ensuring that decision-makers have a clear understanding of what needs to be addressed. This clarity allows them to focus their efforts on finding the most effective solution.
- Comprehensive Information Gathering: By following the strategic decision model, businesses are encouraged to gather and analyze relevant information from various sources. This comprehensive approach ensures that decision-makers have access to accurate and up-to-date data, enabling them to make informed choices based on solid evidence rather than assumptions or guesswork.
- Evaluation of Alternatives: The strategic decision model prompts businesses to generate multiple alternatives or solutions. By evaluating these alternatives against specific criteria such as feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and potential risks, businesses can objectively assess each option’s strengths and weaknesses. This evaluation process enhances decision quality by considering multiple perspectives and reducing biases.
- Alignment with Goals: One of the critical aspects of the strategic decision model is evaluating alternatives based on their alignment with business goals and objectives. This ensures that decisions are made in line with the long-term vision and strategy of the organization, reducing the risk of making choices that may divert resources or deviate from core objectives.
- Risk Management: Strategic decisions often involve risks, but a well-executed strategic decision model helps businesses identify potential risks associated with each alternative early on in the process. By considering these risks during evaluation, businesses can develop mitigation strategies or contingency plans to minimize negative impacts.
- Implementation Planning: Once a choice is made using the strategic decision model, businesses are guided through developing an action plan for implementation. This includes setting timelines, allocating resources effectively, and assigning responsibilities to ensure smooth execution.
- Continuous Improvement: The strategic decision model emphasizes ongoing evaluation and adaptation after implementation. By regularly assessing the outcomes of decisions, businesses can identify areas for improvement, learn from their experiences, and adjust their strategies accordingly. This iterative approach allows for continuous improvement and enhances decision-making capabilities over time.
In summary, a strategic decision model provides businesses with a systematic framework to make better decisions by promoting clarity, information gathering, evaluation of alternatives, alignment with goals, risk management, implementation planning, and continuous improvement. By following this model, businesses can enhance their decision-making processes and increase the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes while minimizing risks and uncertainties.
What are the components of a strategic decision model?
A strategic decision model typically consists of several key components that guide the decision-making process. These components include:
- Problem Definition: Clearly defining the problem or opportunity that requires a strategic decision is crucial. This involves identifying the desired outcome, understanding the context, and determining what needs to be resolved or achieved.
- Information Gathering: Gathering relevant information from various sources is essential to make an informed decision. This includes conducting research, analyzing data, seeking expert opinions, and considering past experiences or case studies.
- Alternatives Generation: In this stage, brainstorm and generate multiple alternatives or solutions to address the problem at hand. Encourage creativity and consider both conventional and unconventional options.
- Evaluation Criteria: Establishing specific evaluation criteria helps in objectively assessing each alternative. Criteria may include feasibility, cost-effectiveness, potential risks, alignment with goals, and potential outcomes.
- Evaluation of Alternatives: Assess each alternative against the established evaluation criteria using quantitative and qualitative analysis techniques. This step helps in comparing alternatives objectively and selecting the most suitable option.
- Decision Making: Based on the evaluation of each alternative, make a choice that best aligns with your objectives and has the highest probability of success. Consider any trade-offs or compromises that may be necessary along with their potential consequences.
- Implementation Planning: Develop an action plan outlining the steps required to implement your decision effectively. Assign responsibilities, set timelines, allocate resources, and establish performance metrics to monitor progress.
- Implementation: Execute the action plan according to the established timeline and allocate necessary resources for successful implementation of the chosen alternative.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly evaluate the outcomes of your decision after implementation to assess whether desired results are being achieved. This step allows for adjustments or adaptations if needed.
- Continuous Improvement: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement by learning from past decisions and experiences to enhance future decision-making processes.
By incorporating these components into a strategic decision model, individuals and organizations can navigate complex challenges and make well-informed choices that align with their goals and aspirations.
What are the benefits of using a strategic decision model?
Using a strategic decision model offers several benefits for individuals and organizations. Here are some key advantages:
- Structured Approach: The strategic decision model provides a structured framework that guides decision-makers through a step-by-step process. This helps prevent hasty or impulsive decisions and ensures that all relevant factors are considered.
- Informed Decision-Making: By following the strategic decision model, decision-makers gather and analyze relevant information, consider multiple alternatives, and evaluate potential outcomes. This leads to more informed choices based on facts rather than assumptions or biases.
- Objective Evaluation: The model encourages objective evaluation of alternatives by considering various criteria such as feasibility, cost-effectiveness, risks, and alignment with goals. This reduces the influence of personal biases and increases the likelihood of making rational decisions.
- Increased Confidence: Making decisions can be daunting, especially when faced with complex situations or high-stakes choices. The strategic decision model provides a systematic approach that instills confidence in decision-makers, as they know they have thoroughly considered all relevant aspects before making a choice.
- Alignment with Goals: Strategic decisions should align with long-term goals and aspirations. The model helps ensure that each decision is in line with the overall vision and objectives of an individual or organization. This promotes consistency and coherence in decision-making.
- Risk Mitigation: Strategic decisions often involve risks, but by using the model, decision-makers can assess potential risks associated with each alternative more effectively. This allows for better risk management strategies to be implemented, reducing the likelihood of negative consequences.
- Continuous Improvement: The strategic decision model emphasizes evaluation and adaptation after implementation. Decision-makers can monitor outcomes, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments to enhance future decisions continuously.
- Enhanced Collaboration: When multiple stakeholders are involved in the decision-making process, using a strategic decision model fosters collaboration by providing a common framework for discussion and evaluation. It promotes transparency and ensures that everyone’s perspectives are considered.
In summary, the strategic decision model brings structure, objectivity, and informed analysis to decision-making processes. It empowers individuals and organizations to make better choices that align with their goals, reduce risks, and drive success.
What challenges can arise when using a strategic decision model?
While the Strategic Decision Model is a valuable framework for making informed choices, it is important to acknowledge that challenges can arise during its implementation. Here are some common challenges that decision-makers may encounter:
- Limited Information: Gathering comprehensive and accurate information can be a challenge. In some cases, data may be scarce or difficult to obtain, leading to incomplete or biased analysis. Relying on incomplete information may result in suboptimal decision-making.
- Uncertainty and Risk: The future is inherently uncertain, and strategic decisions often involve a degree of risk. It can be challenging to accurately assess potential outcomes or predict external factors that may impact the decision’s success. Balancing risk and reward requires careful consideration and sometimes involves making decisions with imperfect information.
- Cognitive Biases: Decision-makers are susceptible to cognitive biases that can influence their judgment and lead to irrational decision-making. Biases such as confirmation bias (favoring information that supports pre-existing beliefs) or anchoring bias (relying too heavily on initial information) can hinder objective evaluation of alternatives.
- Organizational Politics: In complex organizations, decision-making processes can be influenced by power dynamics, conflicting interests, and internal politics. These factors may introduce biases or hinder the adoption of optimal solutions. Navigating organizational politics requires diplomacy and careful consideration of various stakeholders’ perspectives.
- Time Constraints: Strategic decisions often have time-sensitive components, requiring timely action and implementation. However, limited time for analysis and evaluation can lead to rushed decisions or overlooking critical details. Balancing the need for timely action with thoroughness is crucial but challenging.
- Resistance to Change: Implementing strategic decisions often involves change management efforts within an organization or personal adjustments in individual contexts. Resistance from stakeholders or individuals affected by the decision can impede successful implementation if not addressed effectively.
- Evaluation Bias: Assessing the outcomes of a strategic decision is essential for learning and improvement; however, biases can influence the evaluation process. Confirmation bias or hindsight bias may cloud judgment and hinder an accurate assessment of the decision’s effectiveness.
Awareness of these challenges is key to mitigating their impact. Decision-makers should strive for transparency, seek diverse perspectives, challenge assumptions, and continuously evaluate and adapt their decision-making processes to overcome these challenges effectively.