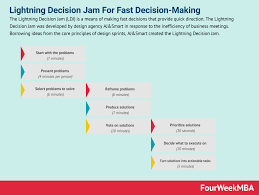
Organizational Strategic Decisions: Examples of Effective Decision-Making
In the ever-evolving landscape of business, organizations face numerous challenges and opportunities that require careful decision-making. One crucial aspect of decision-making within an organization is strategic decision-making. These decisions are pivotal in shaping the long-term direction and success of an organization. Let’s explore some examples of organizational strategic decisions and their significance.
Market Entry Strategy:
When expanding into new markets, organizations must make critical decisions regarding their entry strategy. This includes determining whether to enter through partnerships, acquisitions, or organic growth. For instance, a technology company may decide to acquire a smaller startup to gain access to new technologies and market share quickly. Such strategic decisions can have far-reaching implications on the organization’s growth trajectory.
Product Development:
Organizations often face the challenge of developing innovative products or enhancing existing ones to meet changing customer demands. Strategic decisions related to product development involve choosing which products or features to invest in, considering market trends and competition. For example, a fashion brand may decide to invest in sustainable materials and ethical production practices as part of its product development strategy, aligning with evolving consumer preferences.
Resource Allocation:
Strategically allocating resources is crucial for organizations aiming to optimize their operations efficiently. This involves deciding how much budget should be allocated to different departments or projects based on priorities and potential returns on investment. An organization might allocate more resources towards research and development if it aims to drive innovation or towards marketing if it wants to expand its customer base.
Organizational Structure:
Decisions regarding the organizational structure can significantly impact an organization’s efficiency, communication channels, and decision-making processes. For instance, a company might decide to adopt a flatter hierarchical structure that promotes collaboration and quick decision-making instead of a traditional top-down approach. Such strategic decisions can foster innovation, agility, and adaptability within the organization.
Mergers and Acquisitions:
Strategic decisions related to mergers and acquisitions can reshape the competitive landscape and market positioning of an organization. These decisions involve evaluating potential synergies, market opportunities, and risks. For example, a telecommunications company might decide to merge with a content production company to enhance its service offerings and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Technology Adoption:
In today’s digital age, organizations must make strategic decisions regarding technology adoption to stay competitive. This includes deciding which technologies to invest in, such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, or data analytics. Strategic technology decisions can streamline operations, improve customer experiences, and drive innovation within an organization.
Organizational strategic decisions are complex and require careful analysis of various factors such as market trends, competition, customer preferences, and internal capabilities. These examples highlight the significance of making informed choices that align with an organization’s goals and values.
Effective strategic decision-making involves gathering relevant data, involving key stakeholders in the process, considering multiple perspectives, weighing potential risks and rewards, and aligning decisions with the organization’s long-term vision. By making well-informed strategic decisions, organizations can navigate uncertainties successfully and position themselves for sustainable growth in today’s dynamic business environment.
Common Inquiries Answered: Examples of Organizational Strategic Decisions
- What are strategic decisions examples?
- What is an example of an organizational strategy?
- What are the types of strategic decisions?
- What are strategic decisions in an organization?
What are strategic decisions examples?
Strategic decisions encompass a wide range of choices made by organizations to shape their long-term direction and achieve their goals. Here are some common examples of strategic decisions:
- Market Entry Strategy: Deciding how to enter new markets, such as through partnerships, acquisitions, or organic growth.
- Product Development: Determining which products or features to invest in to meet customer demands and stay competitive.
- Resource Allocation: Strategically allocating budget and resources across departments or projects based on priorities and potential returns on investment.
- Organizational Structure: Deciding on the structure and hierarchy within the organization to optimize efficiency, communication, and decision-making processes.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Evaluating opportunities for mergers or acquisitions to expand market share, gain synergies, or enter new markets.
- Technology Adoption: Making decisions about adopting new technologies that can enhance operations, improve customer experiences, or drive innovation.
- Pricing Strategy: Determining the pricing model for products or services based on market conditions, competition, and value proposition.
- Branding and Marketing Strategy: Developing strategies to position the organization’s brand effectively in the market and reach target customers through marketing channels.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention: Deciding how to attract top talent, develop employee skills, and create a positive work culture that aligns with the organization’s goals.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Making strategic decisions related to environmental sustainability practices, social responsibility efforts, and ethical business practices.
These examples illustrate the diverse nature of strategic decisions that organizations face across different aspects of their operations. Strategic decision-making involves considering internal capabilities, external factors such as market trends and competition, long-term goals, risks versus rewards analysis, and alignment with the organization’s mission and values.
What is an example of an organizational strategy?
An example of an organizational strategy is a company’s decision to focus on product differentiation as a competitive advantage. This strategy aims to distinguish the company’s products or services from competitors in the market.
For instance, a smartphone manufacturer might develop unique features and functionalities that set their devices apart from other brands. This could include advanced camera technology, innovative user interfaces, or exclusive software features. By emphasizing product differentiation as part of their organizational strategy, the company aims to attract customers who value these distinctive qualities and are willing to pay a premium for them.
This strategic decision requires careful planning and allocation of resources towards research and development, design, and marketing efforts. It also involves continuous innovation to stay ahead of competitors and meet evolving customer demands. By implementing this organizational strategy effectively, the company can establish a strong market position and build customer loyalty based on the unique value it offers.
What are the types of strategic decisions?
There are several types of strategic decisions that organizations make to shape their long-term direction and achieve their goals. Here are some common types of strategic decisions:
- Market Entry: Decisions related to entering new markets, expanding geographically, or targeting new customer segments. This includes choosing the mode of entry, such as partnerships, acquisitions, or organic growth.
- Product Development: Decisions regarding the development and enhancement of products or services to meet customer needs and stay competitive. This involves choices about features, functionalities, pricing, and positioning.
- Resource Allocation: Decisions about how to allocate resources such as budget, personnel, and technology across different departments or projects within the organization. This ensures optimal utilization of resources to achieve strategic objectives.
- Organizational Structure: Decisions concerning the design and structure of the organization itself. This includes choices about hierarchical levels, reporting relationships, departmental divisions, and decision-making processes.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Decisions related to combining with or acquiring other companies to achieve strategic objectives like market expansion, gaining access to new technologies or capabilities, or eliminating competition.
- Technology Adoption: Decisions regarding the adoption and implementation of new technologies within the organization. This includes choices about which technologies to invest in based on their potential impact on operations and competitive advantage.
- Strategic Partnerships: Decisions about forming alliances or partnerships with other organizations to leverage complementary strengths and resources for mutual benefit. These partnerships can help expand market reach, share expertise, reduce costs, or drive innovation.
- Diversification: Decisions regarding expanding into new industries or diversifying product/service offerings beyond the organization’s current scope. This can help minimize risks associated with a single market or industry while exploring new growth opportunities.
- Pricing Strategy: Decisions related to setting prices for products/services based on factors such as costs, competition analysis, value proposition, target market dynamics, and profit objectives.
- Branding and Marketing: Decisions regarding brand positioning, marketing channels, messaging, and promotional activities to create awareness, build customer loyalty, and differentiate the organization from competitors.
These are just a few examples of the types of strategic decisions organizations make. The specific types of strategic decisions can vary depending on the industry, market conditions, organizational goals, and other factors that influence the organization’s strategic direction.
What are strategic decisions in an organization?
Strategic decisions in an organization refer to the high-level choices made by top management that shape the overall direction and long-term success of the organization. These decisions are typically complex, impactful, and involve allocating resources to achieve specific goals and objectives. Strategic decisions often have a significant impact on the organization’s competitive position, market presence, financial performance, and overall sustainability.
While operational decisions focus on day-to-day activities and tactical decisions address short-term goals, strategic decisions take a broader perspective and encompass longer time horizons. They involve analyzing internal and external factors, considering market trends, evaluating risks and opportunities, and aligning the organization’s capabilities with its vision.
Strategic decisions can cover various areas within an organization, including:
- Market Entry: Decisions related to entering new markets or expanding existing ones. This may involve choosing target markets, determining market entry strategies (e.g., partnerships, acquisitions), or assessing potential risks and rewards.
- Product Portfolio: Decisions regarding product development, diversification, or discontinuation. These choices involve evaluating customer needs, market trends, competitive analysis, and resource allocation towards product innovation or enhancement.
- Resource Allocation: Determining how resources such as budget, manpower, or technology are allocated across different departments or projects based on priorities and expected returns on investment.
- Organizational Structure: Choices regarding the design of the organizational structure to optimize communication channels, decision-making processes, collaboration among teams or departments.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Evaluating opportunities for mergers or acquisitions to gain market share, expand capabilities or enter new markets while considering potential synergies and risks associated with integration.
- Technology Adoption: Deciding which technologies to invest in to enhance operations efficiency, improve customer experiences or drive innovation within the organization.
- Competitive Positioning: Strategic choices aimed at establishing a unique value proposition in the market by differentiating products/services from competitors through pricing strategies, branding, or market positioning.
Strategic decisions are critical as they guide the organization’s overall direction and influence its ability to adapt to changing environments, seize opportunities, and mitigate risks. These decisions require analysis, foresight, collaboration among key stakeholders, and a deep understanding of the organization’s internal capabilities and external factors impacting its industry.